Figure 3. Loss of PTEN and temozolomide treatment increase the SP fraction; SP cells with PTEN loss are highly tumorigenic.
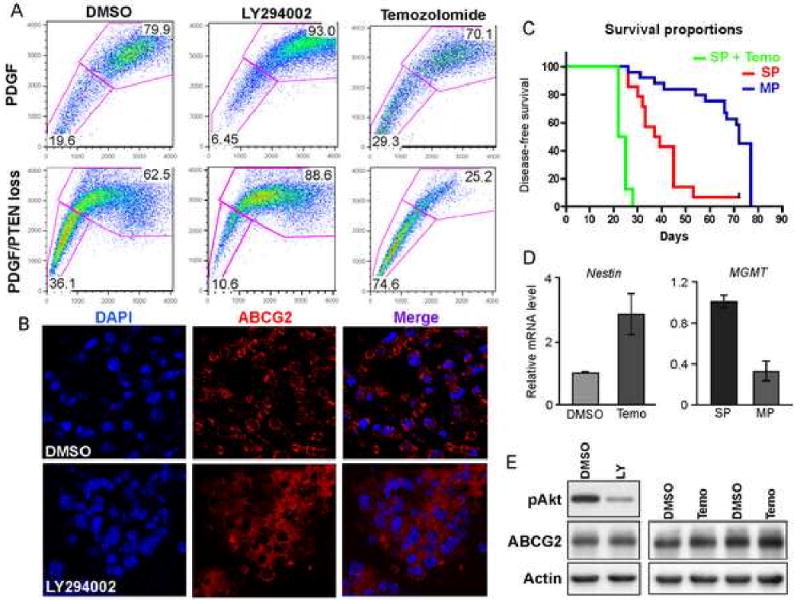
(A) Loss of PTEN in neurospheres strongly increases the SP phenotype, which is partially block by the incubation with the PI3K inhibitor LY294002. Long-term treatment of neurospheres with 100 μM temozolomide induces an increase in the amount of SP cells, which is greatly favored by PTEN deletion.
(B) ABCG2 (red) localizes at the cell membrane in untreated cells as compared to the cytoplasmic staining upon treatment with LY294002.
(C) Kaplan-Meier survival curve shows that SP cells isolated from neurospheres with PTEN loss possess a higher tumorigenic potential than the MP cells; temozolomide treatment increases the tumorigenicity of SP cells.
(D) Q-RT-PCR in neurospheres showing increased nestin expression after treatment with temozolomide; MGMT expression is enriched in SP cells.
(E) Western Blot analysis for ABCG2 indicates that LY294002 (LY) and temozolomide (T) don't modulate ABCG2 expression as compared to DMSO treated cells.
