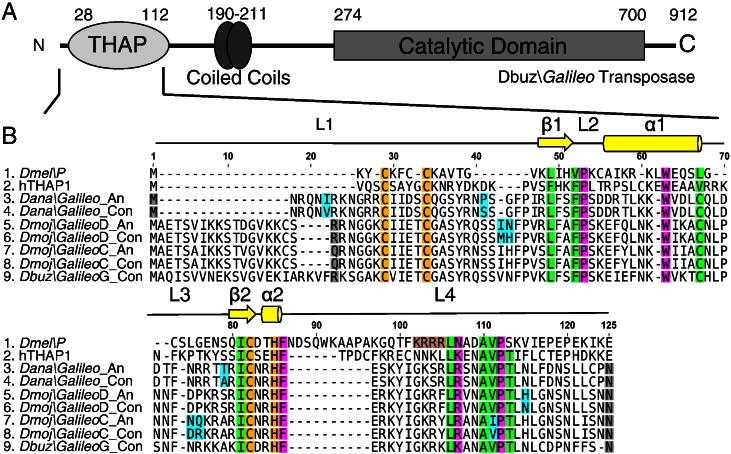
Fig. 2.
THAP domain protein sequences.
A) Domain structure of the predicted Galileo transposase: the THAP is a DNA binding domain, the coiled coil region is probably responsible of protein–protein interactions (represented as two overlapping circles) and the catalytic domain is in the C-terminal region.
B) Alignment of the consensus and ancestral Galileo THAP domain sequences with the THAP domain of the P-element transposase (D. melanogaster) and THAP1 protein (Homo sapiens). The predicted secondary structures are shown above the alignment (adapted from Bessière et al., 2008; Sabogal et al., 2010). Yellow arrows represent β sheets and yellow cylinders are α helical regions. Key residues are colored: yellow: zinc coordination residues (C2CH), green: conserved hydrophobic residues, pink: invariant residues, light brown: nuclear localization signal (NLS) of the P-element transposase. The residues cloned for protein expression are those between the grey shaded ones. The residues colored in cyan are the amino acid changes between ancestor and consensus sequences.