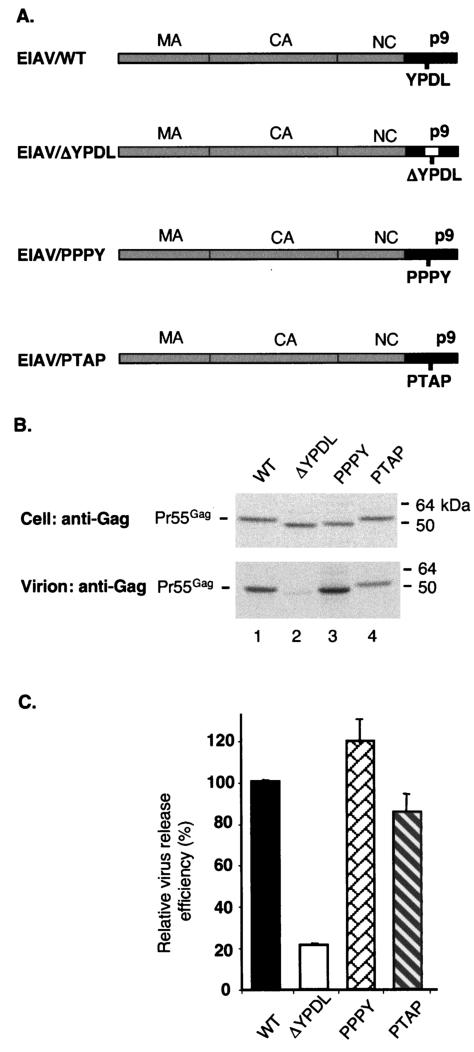
FIG. 1.
The virus budding defect induced by deletion of the YPDL motif in EIAV p9 is reversed by introducing the PPPY or PTAP motif. (A) The schematic organization of the WT and mutant EIAV Gag chimeras used in this study. The location of the L domain of EIAV (YPDL) is shown. The open box within p9 represents the YPDL deletion (ΔYPDL). The EIAV/WT p9 sequence YPDL is replaced by SRSA (EIAV/ΔYPDL), ASAPPPPYVG (EAIV/PPPY), or RPEPTAPP (EIAV/PTAP). CA, capsid protein; NC, nucleocapsid protein. (B) 293T cells were transfected with vectors expressing EIAV/WT Gag, the ΔYPDL deletion mutant, or the PPPY and PTAP chimeras. Transfected cells were metabolically labeled overnight with [35S]Met-[35S]Cys; cell and viral lysates were radioimmunoprecipitated with horse anti-EIAV antiserum (Materials and Methods). The position of the EIAV Gag precursor (Pr55Gag) is indicated on the left, and the position of molecular mass markers is shown on the right. (C) Virus release efficiency, determined by phosphorimager analysis and calculated as the amount of VLP-associated Gag divided by the total (cell plus VLP) Gag. The data are averages from at least three independent experiments plus or minus the standard error.