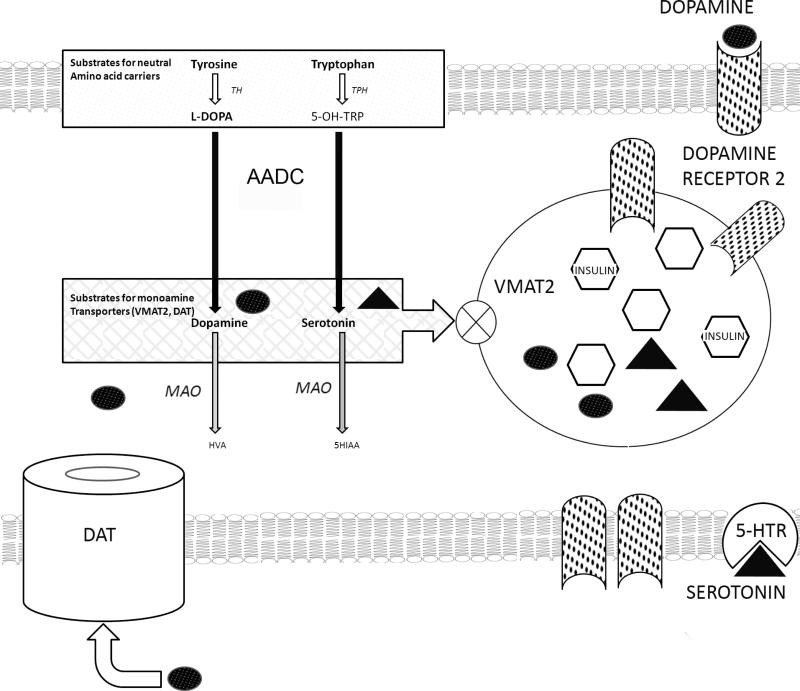
Figure 1.
Schematic of a putative dopamine mediated autocrine negative feedback circuit in β-cells. Import of aromatic amino acids (Tyrosine [Try] and Tryptophan [Trp]) by neutral amino acid carriers (LAT1) from extracellular space occurs, followed by transformation of Typ and Trp to L-DOPA and 5-hydroxy-tryptophan (5-OH-TRP) by the action of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH). Both L-DOPA and 5-OH-TRP are transformed into dopamine (DA) and serotonin (5-HT) by the action of aromatic amino acid decarboxylase (AADC).Cytoplasmic DA or 5-HT are transported by VMAT2 into β-cell vesicles and later delivered to the intracellular space following glucose stimulated insulin secretion. Dopamine type 2 receptors are stored in vesicles, rendered inactive in the acid microenvironment. Extracellular dopamine (e.g. as elevated dopamine sulfate found in postprandial serum samples can shuttled inside the β-cell by the action of the dopamine transporter (DAT). DA and 5-HT not sequestered by the action of VMAT2 is exposed to the action of monoamine oxidase and destructively metabolized.