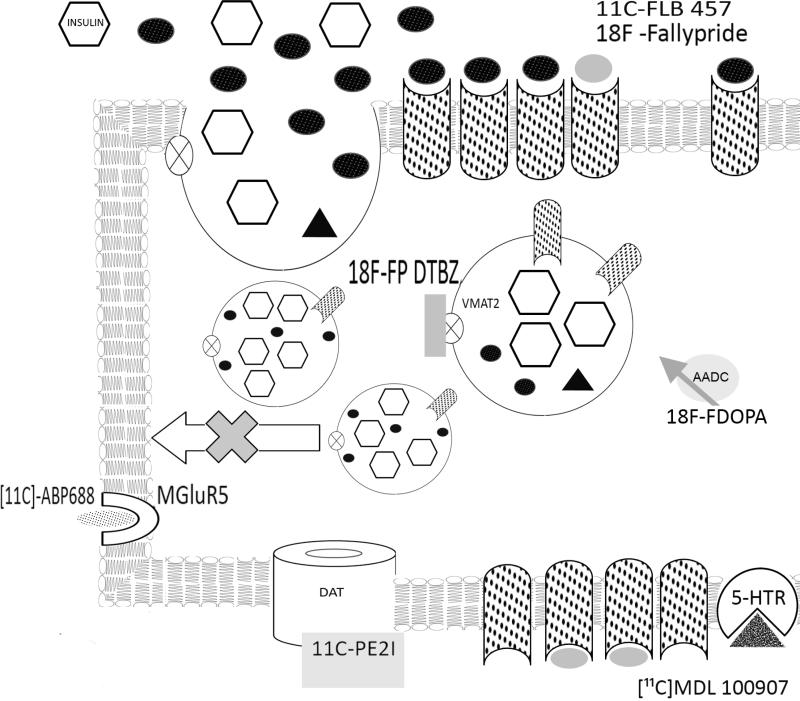
Figure 2.
Upon glucose stimulation, insulin (open hexagons), dopamine (black ovals) and dopamine type 2 receptors (stippled) are delivered to the extracellular space or plasma membrane. Dopamine diffuses to active cell surface D2R or D2R expressed on neighboring β-cell and binds to dopamine receptor (D2R) inhibiting further insulin secretion. The dopamine receptor type 2 PET ligands [11C]-FLB457 or 18F-Fallypride are shown in grey ovals. The VMAT2 antagonist dihydrotetrabenazine (DTBZ) prevents vesicular storage of dopamine by high affinity binding near the monoamine binding site. The VMAT2 PET ligand 18F-FP-DTBZ (grey rectangle) is shown bound to VMAT2 (open circle with X). The tyrosine hydroxylase substrate and PET ligand 18FDOPA is shown adjacent to its enzyme.PET ligands for the metabotropic glutamate receptor, 11C-APB 688 (stippled oval bound to open reversed C); dopamine transporter, 11C-PE2I; ( grey rectangle bound to open doughnut) and serotonin receptor 5HT2A, 11C MDL 100907( stippled triangle bound to open pie) are also shown.