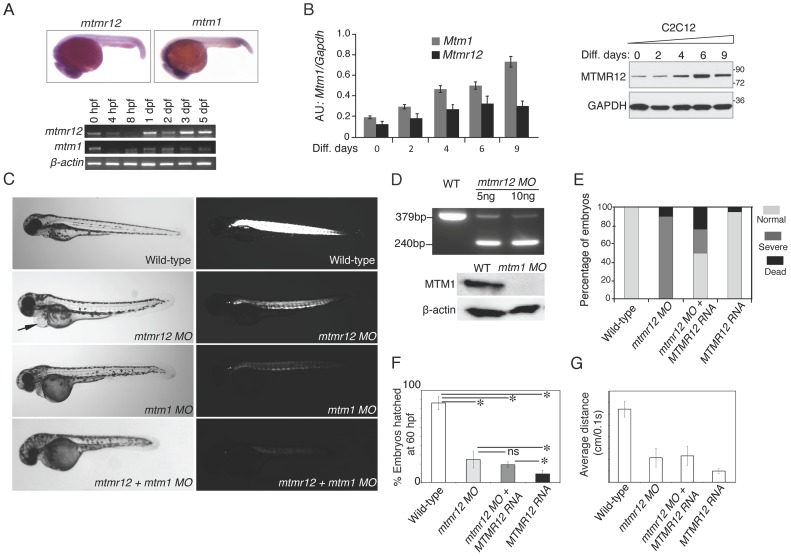
Figure 2. Expression patterns and morpholino-based knockdown of mtmr12 in developing zebrafish.
(A) Whole mount in-situ hybridization detected ubiquitous expression of mtmr12 and mtm1 transcripts in zebrafish embryos at 1 dpf (above). Below is RT-PCR analysis of mtm1 and mtmr12 expression during zebrafish development using RNA extracts from whole zebrafish embryos at indicated developmental timepoints. (B) Synergistic expression level of Mtm1 and Mtmr12 transcripts and protein at indicated time points of C2C12 differentiation (0–9 days) monitored by RT-quantitative PCR (corresponding histogram, *P≤0.05) and by western blot analysis (right panel). (C) Live embryos at 3 dpf injected with control, mtmr12, mtm1 or both mtmr12 and mtm1 morpholinos in normal (left) and polarized lights (right). mtmr12 morphant fish showed a dorsal curvature in skeletal muscle and reduced birefringence in polarized light similar to mtm1 morphant embryos. mtmr12 morphant fish also exhibited pericardial edema (arrow). mtmr12-mtm1 double knockdown fish exhibited smaller size and reduced birefringence relative to mtm1 or mtmr12 alone morphant fish. (D) mtmr12 mRNA levels in mtmr12 morphant zebrafish following injection of two different amounts of morpholino (indicated below, upper panel). In mtm1 morphant fish, no residual myotubularin was observed showing that mtm1 morpholinos are completely penetrant to the limits of detection for western blotting. (E) Over-expression of human MTMR12 mRNA rescued small body length and skeletal muscle abnormalities observed in mtmr12 morphant embryos. (F) Quantification of the chorion hatching at 60 hpf. The number of embryos was quantified in three independent clutches (number of embryos in each clutch = 90–120). (G) Quantification of touch evoke response at 3 dpf (n = 5–8 embryos were assayed in each morpholino group).*P≤0.01.