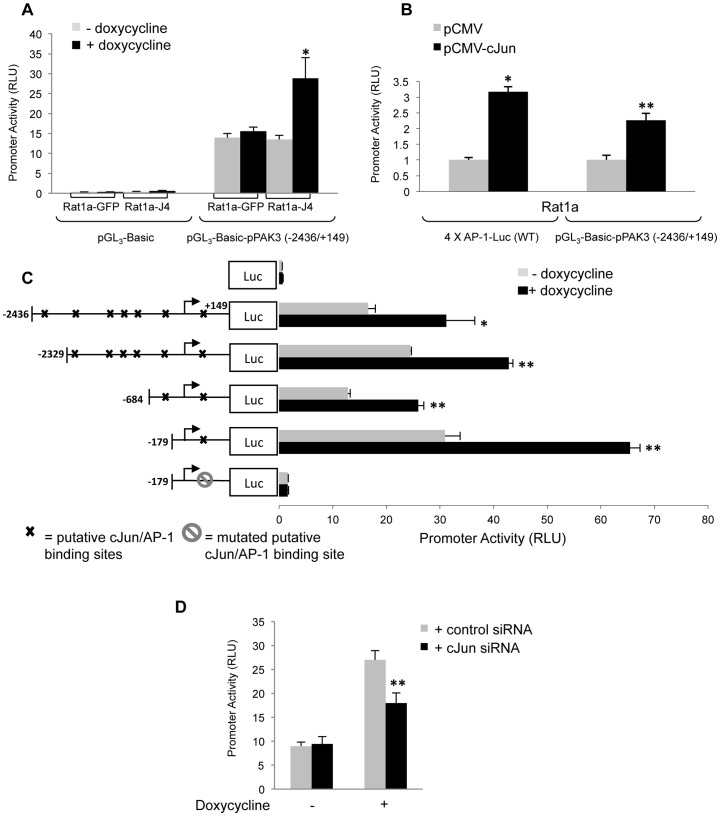
Figure 2. cJun/AP-1 over-expression causes increased PAK3 promoter activity via a binding site at position (+52/+60).
The (−2436/+149) region of the PAK3 promoter, containing several putative cJun/AP- binding sites, was cloned into the pGL3-Basic reporter vector. A: Luciferase promoter reporter assays performed in control cells, Rat1a-GFP, and Rat1a-J4 cells transiently transfected with empty vector, pGL3-Basic, and PAK3 promoter construct containing vector, pGL3-Basic-pPAK3 (−2436/+149). Cells were grown in the absence and presence of doxycycline. B: Luciferase promoter reporter assays performed in the parental rat fibroblast cell line, Rat1a, transfected with either pCMV-cJun or empty pCMV vector with the PAK3 promoter construct containing vector, pGL3-Basic-pPAK3 (−2436/+149). A plasmid containing four AP-1 binding sites, 4 X AP-1-Luc, was used as a control showing cJun activation. C: Luciferase reporter promoter assays for deletion constructs of the PAK3 promoter region (−2436/+149), (−2329/+149), (−684/+149) and (−179/+149) as well as a (−179/+149) with a mutated cJun/AP-1 binding site at position (+52/+60), in the presence and absence of doxycycline-induced cJun/AP-1 expression. D: Luciferase reporter assays, using the (−179/+149) PAK3 promoter construct, showing the effect of transient cJun inhibition on PAK3 promoter activity in the absence and presence of doxycycline induced cJun/AP-1 over-expression. Results show the mean±S.E. of experiments performed in triplicate and repeated at least three times. (*p≤0.05 and **p≤0.01).