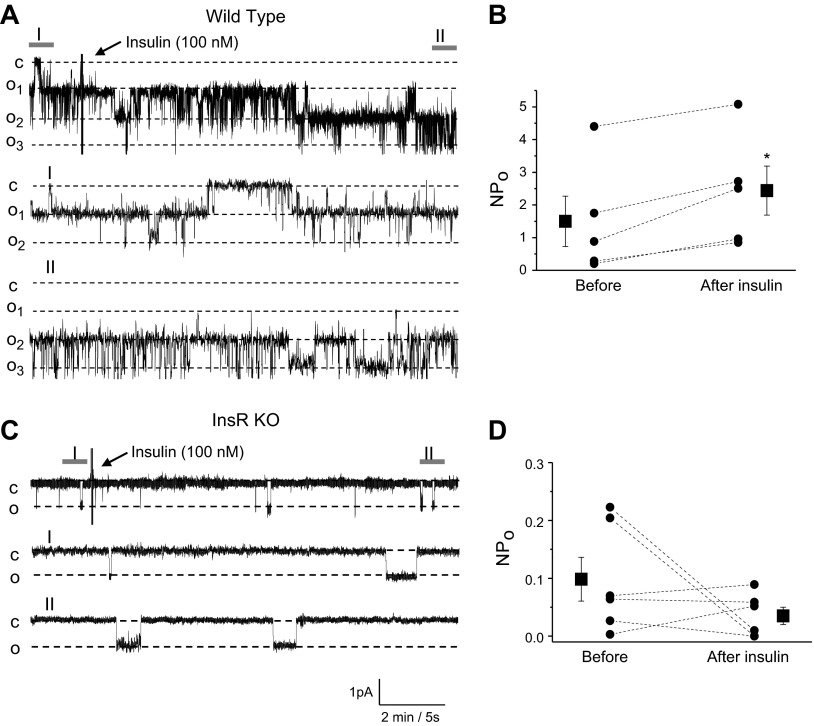
Figure 7.
Insulin acutely increases ENaC activity in CCDs via InsR. A, C) Effect of insulin on ENaC activity in freshly isolated CCDs of WT (A) and InsR-KO mice (C). Continuous current traces from representative cell-attached patches were recorded on the apical membrane of principal cells before and after treatment with insulin (100 nM). Areas before (I) and after (II) treatment are shown at middle and bottom with an expanded time scale. These patches were held at a −60 mV test potential during the course of the experiment. c, closed current level; on, open current level. B, D) Summary graphs of ENaC NPo changes from WT (B) and InsR-KO mice (D) in response to insulin application in patch-clamp experiments similar to those shown in panels A and C. *P < 0.05 vs. before insulin application.