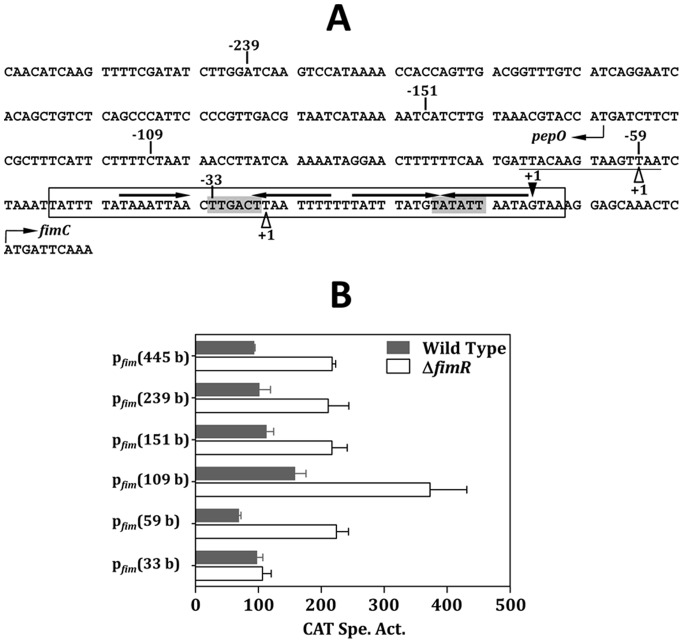
Figure 2. The regulation of FimR on pfim expression.
(A) The nt sequence of the 5′ flanking region of fimC. The pepO and fimC are transcribed from the opposite DNA strands, thus the sequence of pepO presented here is the noncoding strand, and the sequence of fimC is the coding strand. The transcription initiation sites (+1) of fimC and pepO are shown by a solid triangle above the sequence, and two open triangles below the sequence, respectively. The putative −10 and −35 sequences of pfim are shaded. The potential Per box is underlined. The inverted repeat sequences are shown by horizontal arrows above the sequence. The sequence of the probe used in EMSA is boxed. The limits of the deletion derivatives are indicated by the numbers. (B) The CAT activities in wild-type FW213 and ΔfimR harboring various pfim-cat fusions. All strains were grown in TH. Values shown are means and standard deviations of three independent experiments. All experiments were done in triplicate reactions and negative controls were reactions carried out in the absence of Cm.