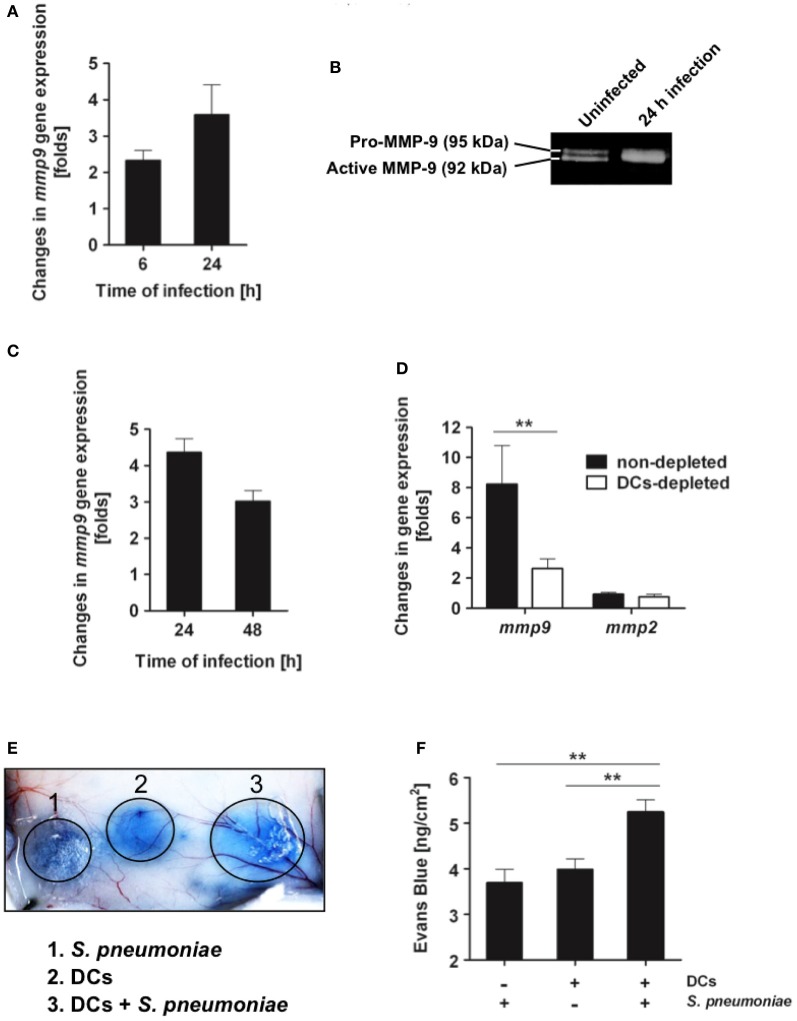
Figure 8.
S. pneumoniae triggers production of MMP-9 on in vitro cultured DCs and in lung tissue during in vivo infection. (A) Bone marrow-derived DCs were infected with S. pneumoniae (MOI 20:1), RNA was extracted from DCs at 6 and 24 h postinfection and subjected to real-time PCR for quantification of mmp-9 gene expression. Results are expressed as fold-change in MMP-9 mRNA of infected DCs over the amount of MMP-9 mRNA in uninfected DCs. Each bar represents the mean of three independent experiments. (B) Representative gelatin zymography demonstrating the up-regulation of the active form of MMP-9 in the supernatant of S. pneumoniae-infected DCs at 24 h postinfection. (C) Up-regulation of mmp-9 gene expression in the lungs of BALB/c mice during infection with S. pneumoniae. BALB/c mice were intranasally infected with 1 × 108 CFU of S. pneumoniae D39, the RNA was isolated from the lungs at 24 and 48 h of infection and subjected to real-time PCR for detection of MMP-9 mRNA. Each bar represents the mean value of three independent experiments. (D) Up-regulation of mmp-9 gene expression in the lungs of DCs-depleted (white bar) or non-depleted (black bar) CD11c-DTR chimera mice at 24 h of infection with 1 × 108 CFU of S. pneumoniae D39. Each bar represents the mean value of three independent experiments. (E) Vascular permeability induced by the supernatant from either S. pneumoniae (1), DCs (2), or S. pneumoniae-infected DCs (24 h postinfection) (3). Supernatant (50 μl) was intradermally applied into the skin of Evans blue-treated mice and vascular leakage of Evans blue was visualized 1 h thereafter. A representative experiment out of three is shown. (F) Quantification of Evans blue leakage in the skin of mice after application of supernatant from S. pneumoniae, DCs or S. pneumoniae-infected DCs (24 h postinfection). Each bar represents the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. **p < 0.01.