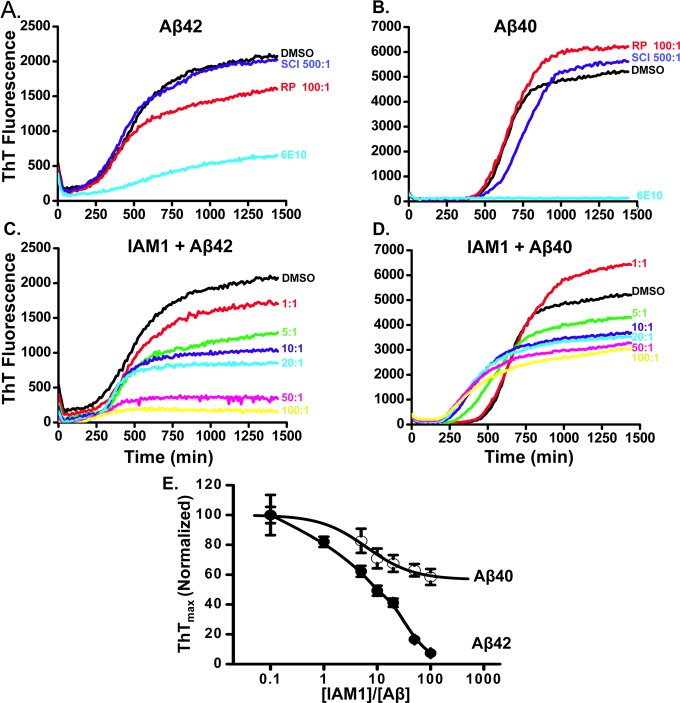
Figure 3.
Inhibitory ability of IAM1 toward the aggregation of Aβ42 and Aβ40 using the in situ kinetic thioflavin T (ThT) assay. (A, B) Time course of the fluorescence of aggregate-bound ThT in the presence of Aβ42 (A) or Aβ40 (B) and different compounds. The RP (100:1) was used as a negative control and anti-Aβ antibody 6E10 (20-fold dilution) as a positive control. The scyllo-Inositol (500:1) was used as a reference compound. (C, D) Time courses of the fluorescence of aggregate-bound ThT in the aggregation processes of Aβ42 (C) or Aβ40 (D) in the presence of IAM1 at different concentrations. Molar ratio of IAM1:Aβ in the range from 1:1 to 100:1 as indicated. (E) The normalized ThTmax values for the Aβ42 and Aβ40 aggregation processes are plotted as a function of IAM1 concentration. The data in each aggregation experiment were normalized to the ThTmax value obtained in the presence of DMSO, averaged and shown as mean ± SEM (n = 3).