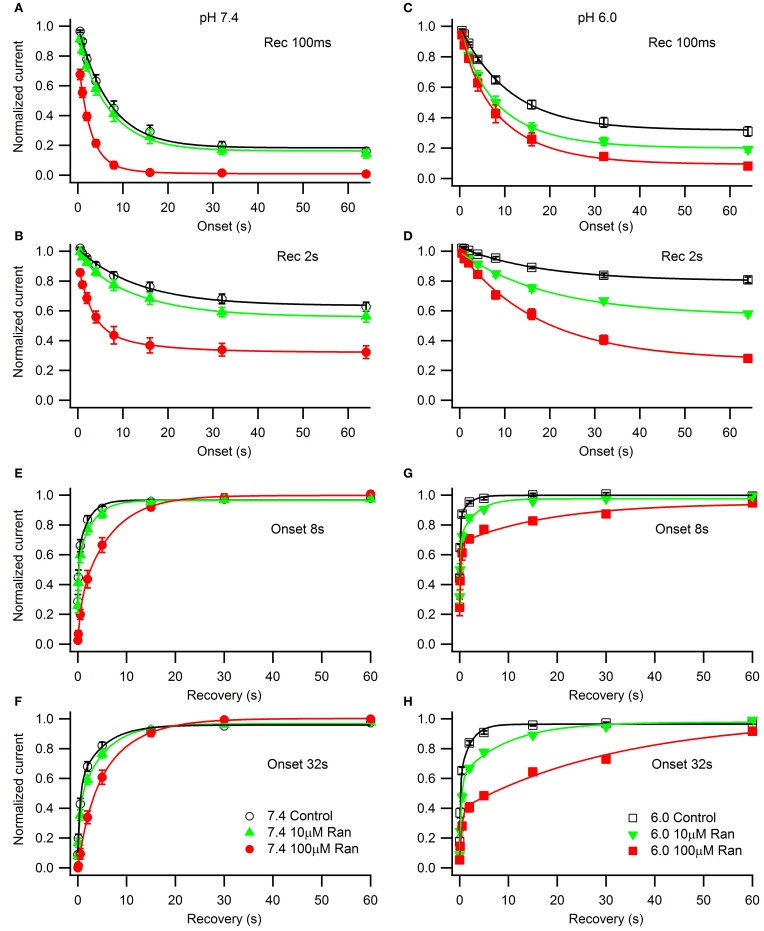
Figure 8.
Slow inactivation onset and recovery and effects of ranolazine at pH 7.4 (left) and 6.0 (right). Onset of slow inactivation (A–D) was induced by conditioning pulses to −10 mV ranging from 500 ms to 64 s. Amount of slow-inactivated channels (control, open black symbols) or a combination of slow-inactivated and ranolazine blocked channels (closed symbols) was assessed by 5 ms test pulses to −10 mV after either 100 ms (A,C) or 2 s (B,D) recovery at −130 mV. Onset kinetics were fitted with a single exponential function for control conditions and with a double exponential function for ranolazine conditions. Fit parameters are summarized in Table A7. Slow inactivation and ranolazine block recovery (E–H) was measured with a series of 5 ms test pulses ranged from 20 ms to 60 s after either 8 s (E,G) or 32 s (F,H) onset. Recovery followed double exponential kinetics in all conditions. Fit parameters are summarized in Table A8.