Table 2.
Scope of Enantioselective Hydroaminationa
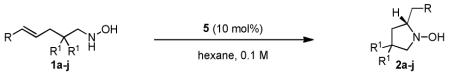
| entry | R | R1 | product | time (h) | temp (d°C) | yieldb | eec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C6H5 | Me | 2a | 12 | 3 | 83 | 94 |
| 2d | C6H5 | Me | 2a | 72 | 3 | 79 | 92 |
| 3 | p-ClC6H4 | Me | 2b | 5 | 3 | 87 | 95 |
| 4 | p-(Me)C6H4 | Me | 2c | 36 | 3 | 84 | 87 |
| 5 | p-(OMe)C6H4 | Me | 2d | 96 | 3 | 96 | 91 |
| 6 | o-ClC6H4 | Me | 2e | 5 | 3 | 91 | 92 |
| 7 | m-ClC6H4 | Me | 2f | 5 | 3 | 87 | 94 |
| 8 | C6H5 | -CH2(CH2)3CH2- | 2g | 5 | 3 | 82 | 96 |
| 9 | C6H5 | H | 2h | 72 | 30 | 68 | 81 |
| 10 | p-ClC6H4 | H | 2i | 36 | 30 | 93 | 83 |
| 11 | H | Me | 2j | 2 | 3 | 86 | 78 |
| 12e | H | Me | 2j | 2 | 3 | 91 | 85 |
Reactions were performed on a 0.18–0.25 mmol scale, and were quenched by the addition of p-NO2 benzoyl chloride. For entries 1–3, 6–8, and 11–12 the hydroxylamine was generated in situ from the corresponding trifluoroacetate salt by addition of aqueous potassium carbonate.
Isolated yields of O-benzoylated products after purification on silica gel.
Determined by HPLC analysis of O-benzoylated products using commercial chiral columns.
mol% of 5 was used.
10 mol% of 3e was used as the catalyst.
