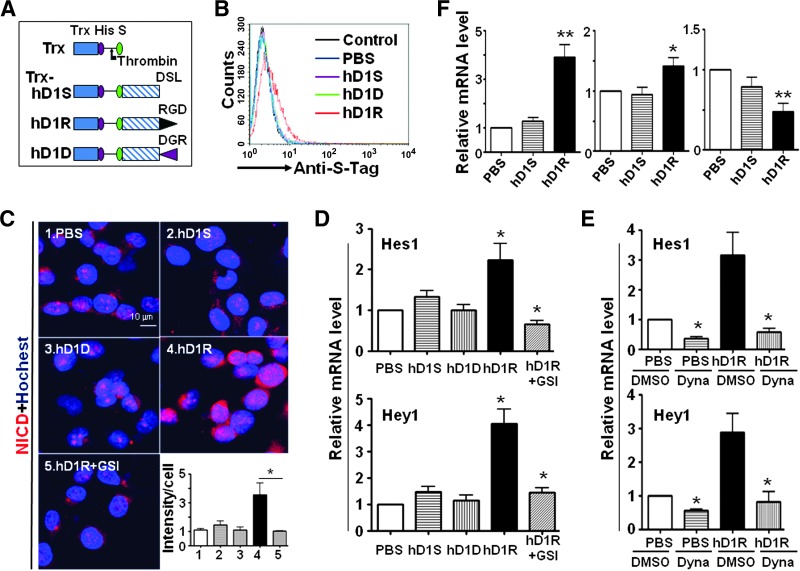
Figure 1.
EC-targeted hDll1 efficiently activated Notch signaling. (A) Schematic representatives of recombinant proteins. Trx, His, S, DSL, RGD, and DGR indicate thioredoxin, His tag, S tag, DSL domain of hDll1, RGD peptide, and DGR peptide, respectively. The site of thrombin cleavage is indicated with an arrow. (B) HUVECs were incubated with PBS, hD1S, hD1R, or hD1D and examined by FACS after secondary staining with anti-S-Tag. (C) hD1R activates Notch signaling in RGD- and GSI-dependent ways. HUVECs were incubated with PBS, hD1S, hD1R, or hD1D for 24 hours. GSI was included in some of the cultures as indicated. Cells were stained by immunofluorescence using anti-NICD. The intensity of fluorescent signals per cell was quantified and shown in the inset. (D) HUVECs were treated as in C. Cells were harvested and the expressions of Hes1 and Hey1 were detected by quantitative RT-PCR. (E) Activation of Notch signaling by hD1R required endocytosis. HUVECs were incubated with PBS or hD1R for 24 hours. DMSO or Dynasore was included in the medium as indicated. The expression of Hes1 and Hey1 was detected by using quantitative RT-PCR. (F) Activation of endothelial Notch signaling by hD1R in vivo. P3 pups were injected daily s.c. with PBS, hD1S, or hD1R. On P7, the retinas of the pups were collected and used for real-time RT-PCR for the expression of Hes1, VEGFR1, and VEGFR2, with CD31 as a reference control. Bars, means ± SD. *P < .05, **P < .01, n = 5.