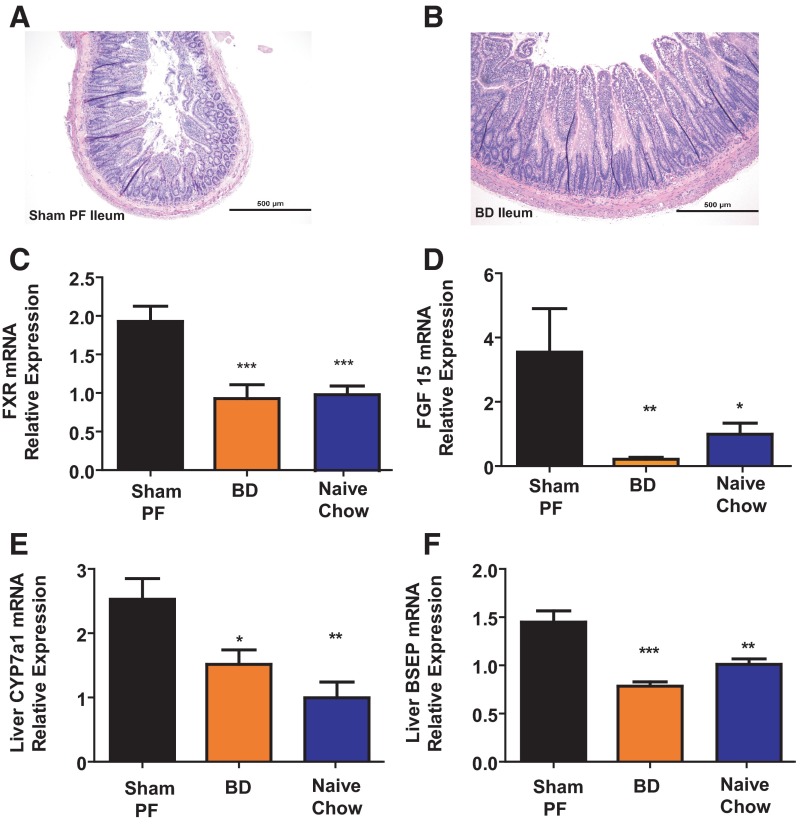
Figure 4.
A, Ileal histology after surgery. Rats humanely destroyed 5 weeks after surgery from the BD group showed histologic adaptation of the ileum. Hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections) (magnification, times]10)of the BD rat's ileum at time of death shows marked increase in length and number of villi compared with the SH-PF (B) animals ileal histology, which has remained typical of a rat ileal with short villi length. C, Response of ileal epithelial bile acid-responsive gene FXR. mRNA levels of bile acid-responsive nuclear receptor gene FXR were measured by RT-PCR and expressed in relative expression units. FXR mRNA was decreased in BD rats compared with SH-PF. N for groups: BD = 7; SH-PF = 5; Chow Naive = 5 (ANOVA, Post hoc Tukey's: ***, P < .001). D, Fecal bile acid quantification. Using a 3-day fecal collection, total fecal bile acid levels were measured and found to be similar in BD rats compared with all other groups including weight-matched Chow Naïve and food-intake-matched SH-PF. E, Hepatic bile acid production. mRNA levels of the gene coding for the rate-limiting bile acid production enzyme 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) were measured by RT-PCR and expressed in relative expression units. CYP7A1 mRNA was decreased in BD rats compared with SH-PF. N for groups: BD = 6; SH-PF = 4; Naïve-Chow = 6 (ANOVA, post hoc Tukey's: *, P < .05; **, P < .01). F, Hepatic bile acid export. mRNA levels of the gene coding for the major BSEP and OATPs were measured by RT-PCR and expressed in relative expression units. BSEP and OATPs mRNA were decreased in BD rats compared with SH-PF. BD = 6, SH-PF = 4, Naïve-Chow = 6 (ANOVA, post hoc Tukey's: **, P < .01; ***, P < .001).