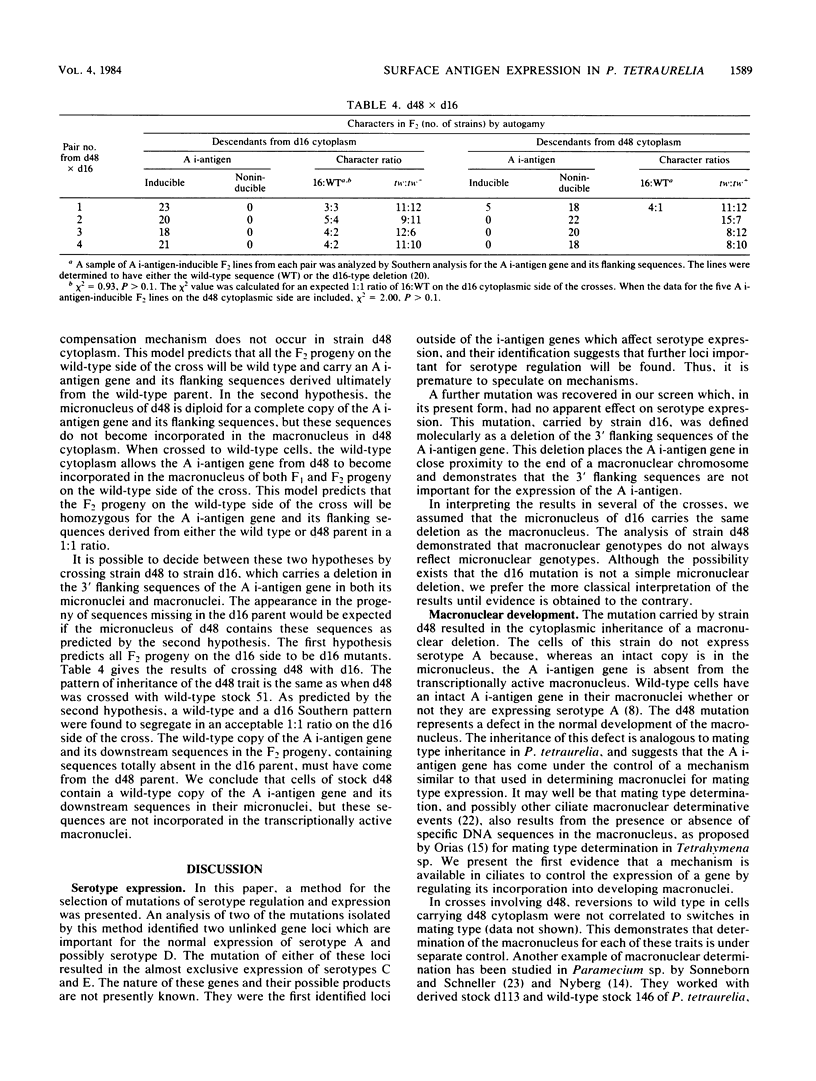
Abstract
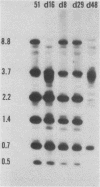
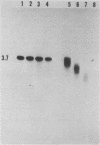
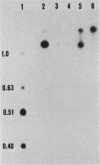
A screening procedure was devised for the isolation of X-ray-induced mutations affecting the expression of the A immobilization antigen (i-antigen) in Paramecium tetraurelia. Two of the mutations isolated by this procedure proved to be in modifier genes. The two genes are unlinked to each other and unlinked to the structural A i-antigen gene. These are the first modifier genes identified in a Paramecium sp. that affect surface antigen expression. Another mutation was found to be a deletion of sequences just downstream from the A i-antigen gene. In cells carrying this mutation, the A i-antigen gene lies in close proximity to the end of a macronuclear chromosome. The expression of the A i-antigen is not affected in these cells, demonstrating that downstream sequences are not important for the regulation and expression of the A i-antigen gene. A stable cell line was also recovered which shows non-Mendelian inheritance of a macronuclear deletion of the A i-antigen gene. This mutant does not contain the gene in its macronucleus, but contains a complete copy of the gene in its micronucleus. In the cytoplasm of wild-type animals, the micronuclear gene is included in the developing macronucleus; in the cytoplasm of the mutant, the incorporation of the A i-antigen gene into the macronucleus is inhibited. This is the first evidence that a mechanism is available in ciliates to control the expression of a gene by regulating its incorporation into developing macronuclei.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst P., Cross G. A. Molecular basis for trypanosome antigenic variation. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):291–303. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brink R. A., Styles E. D., Axtell J. D. Paramutation: directed genetic change. Paramutation occurs in somatic cells and heritably alters the functional state of a locus. Science. 1968 Jan 12;159(3811):161–170. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3811.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIPPELL R. V. A temporary stain for Paramecium and other ciliate protozoa. Stain Technol. 1955 Mar;30(2):69–71. doi: 10.3109/10520295509113746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Huang H., Davis M., Calame K., Hood L. An immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene is generated from three segments of DNA: VH, D and JH. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):981–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forney J. D., Epstein L. M., Preer L. B., Rudman B. M., Widmayer D. J., Klein W. H., Preer J. R., Jr Structure and expression of genes for surface proteins in Paramecium. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;3(3):466–474. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.3.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray H. B., Jr, Ostrander D. A., Hodnett J. L., Legerski R. J., Robberson D. L. Extracellular nucleases of Pseudomonas BAL 31. I. Characterization of single strand-specific deoxyriboendonuclease and double-strand deoxyriboexonuclease activities. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Sep;2(9):1459–1492. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.9.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidwell M. G. Hybrid Dysgenesis in DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER: Factors Affecting Chromosomal Contamination in the P-M System. Genetics. 1983 Jun;104(2):317–341. doi: 10.1093/genetics/104.2.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim J. K., Simmons M. J., Raymond J. D., Cox N. M., Doll R. F., Culbert T. P. Homologue destabilization by a putative transposable element in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6624–6627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. F., Mlawer N., So M. Pilus expression in Neisseria gonorrhoeae involves chromosomal rearrangement. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyberg D. Alternative Phenotypic States in Genomically Identical Cells: Interstock Genetics of a Trichocyst Phenotype in PARAMECIUM TETRAURELIA. Genetics. 1980 Apr;94(4):933–950. doi: 10.1093/genetics/94.4.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer J. R., Preer L. B., Rudman B. M. mRNAs for the immobilization antigens of Paramecium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6776–6778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonneborn T. M. Genetics of cellular differentiation: stable nuclear differentiation in eucaryotic unicells. Annu Rev Genet. 1977;11:349–367. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.11.120177.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonneborn T. M. The Determination of Hereditary Antigenic Differences in Genically Identical Paramecium Cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1948 Aug;34(8):413–418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.34.8.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathern J. N., Spatola E., McGill C., Hicks J. B. Structure and organization of transposable mating type cassettes in Saccharomyces yeasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2839–2843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieg J., Hilmen M., Simon M. Regulation of gene expression by site-specific inversion. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90098-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Putte P., Cramer S., Giphart-Gassler M. Invertible DNA determines host specificity of bacteriophage mu. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):218–222. doi: 10.1038/286218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]