Figure 6. Potassium binding site in PaMurB and its proposed role in catalysis.
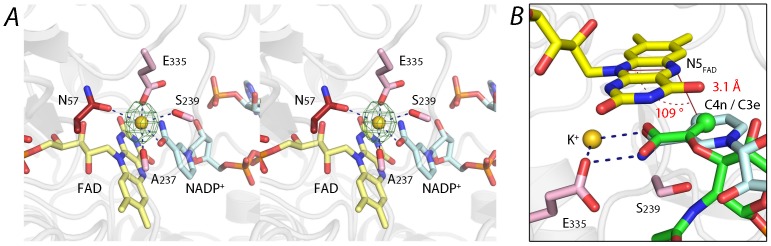
A. Structure of the potassium binding site in PaMurB crystal form A. The coordination sphere is formed by the carboxamide oxygen of NADP+ nicotinamide in addition to two side chain oxygens and two main chain oxygens from the protein. The potassium ion (gold sphere) and its Fo-Fc omit difference density contoured at 5.0 σ (green mesh) are shown. B. The active site potassium ion assists in substrate orientation and binding. Superimposition of the PaMurB crystal form A structure and the EcMurB-UNAGEP complex (PDB code 2MBR) based on FAD atomic coordinates shows that the C2-C3-C4 locus of NADP+ nicotinamide (in cyan) spatially overlap with the enolpyruvyl group of UNAGEP (in green). Both substrate moieties are bound to Glu-335 and the backbone amine of Ser-239. The nicotinamide C4n atom (cyan sphere), which transfers a hydride to the isoalloxazine N5 atom, coincides with the enolpyruvyl C3e (green sphere), which receives the hydride during the second half-reaction. The geometric relation of the C4n atom to the isoalloxazine is indicated. In synergy with the isoalloxazine ring, Glu-335 and Ser-239, the potassium ion positions NADPH and UNAGEP such that the substrate carbons are in the optimal position for hydride transfer.
