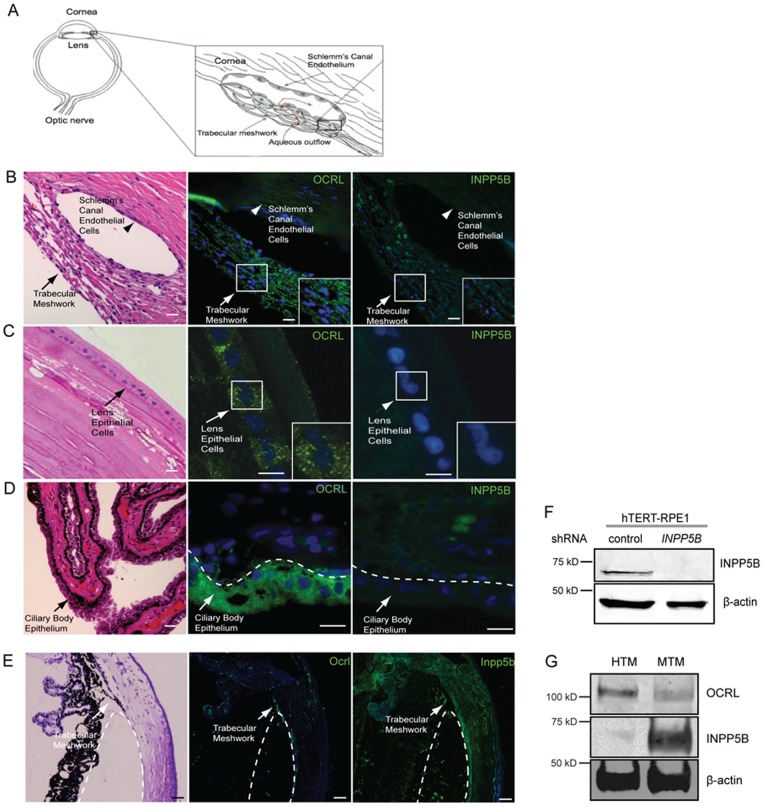
Figure 1. Localization of OCRL and INPP5B in human ocular tissue.
(A) Diagram of trabecular meshwork and Schlemm’s canal endothelial cells (aqueous flow, red; trabecular meshwork, arrow; Schlemm’s canal endothelial cells, arrowhead). (B) Human eye sectioned and stained by H&E or immunofluorescence with anti-OCRL (green) or anti-INPP5B antibody (green), and DAPI (blue). Staining of trabecular meshwork cells in vesicular pattern (insert, arrow) and Schlemm’s canal (arrowhead). Scale bar 10 micron. (C) Lens epithelial cells (arrow) stained with H&E, anti-OCRL antibody (green) or anti-INPP5B antibody (green), and DAPI (blue). Scale bar 10 micron. (D) Ciliary body epithelial (arrowhead) cells stained with H&E, anti-OCRL antibody (green) or anti-INPP5B antibody (green), and DAPI (blue). Scale bar 10 micron. (E) Mouse eye sectioned and stained with H&E, anti-OCRL antibody (green) or anti-INPP5B antibody (green), and DAPI (blue). Staining of trabecular meshwork cells in vesicular pattern (dash line indicates border of trabecular meshwork). Scale bar 10 micron. (F) Immunoblot of INPP5B expression in 30 microgram lysates of hTERT-RPE1 shRNA knockdown cells compared to beta-actin. (G) Immunoblot analysis of 40 microgram lysates of human and mouse trabecular meshwork with anti-OCRL, anti-INPP5B and anti-beta-actin antibodies.