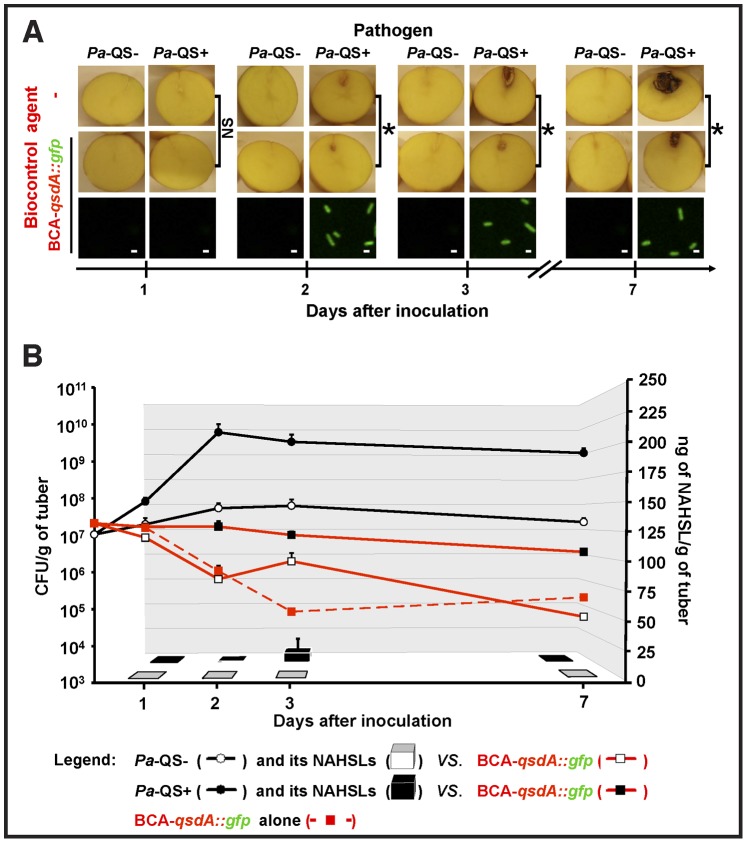
Figure 1. Induction ofqsdA gene transcription, NAHSL-breakdown and biocontrol activity of R. erythropolis in potato tubers.
(A) qsdA gene transcription and biocontrol activity of the R. erythropolis BCA-qsdA::gfp against P. atrosepticum 6276 defective (Pa-QS–) or not (Pa-QS+) for NAHSL production were analyzed at 1, 2, 3 and 7 days after inoculation of S. tuberosum var. Allians tubers. For the controls, one of the two strains was replaced in the inoculum with a 0.9% NaCl solution. Asterisks indicate significantly less severe maceration symptoms in the presence of the BCA-qsdA::gfp, as assessed with the Mann and Whitney test (α = 0.05). The fluorescence of the BCA-qsdA::gfp was analyzed by confocal laser scanning microscopy. (B) The numbers of P. atrosepticum (black lines) and R. erythropolis (red lines) bacteria per unit weight (CFU/g fresh weight of potato tubers), and NAHSL concentration (ng/g of potato tubers; black and white bars) were determined for each condition in potato tubers. For lines and bars, each value is the mean of three replicates with the standard deviation indicated. NS, non-significant; NAHSL, N-acyl homoserine lactone.