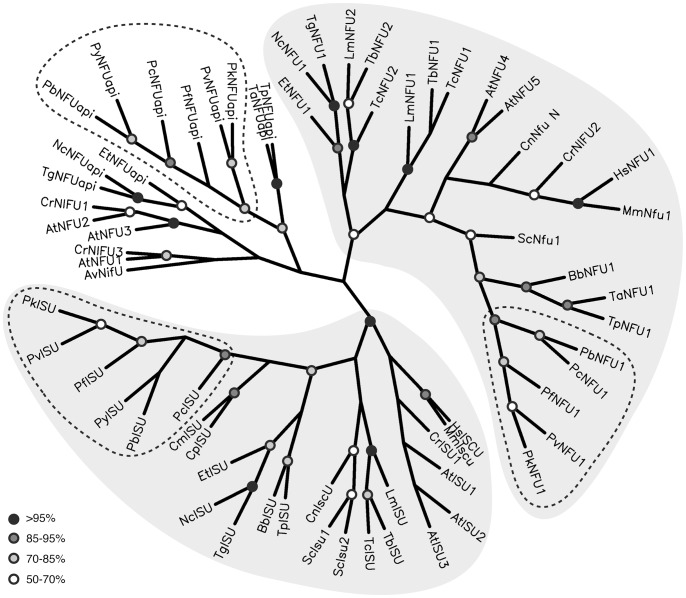
Figure 2. Phylogenetic analysis of apicomplexan and other representative eukaryotic NifU-like domain containing proteins.
Maximum likelihood distances were calculated for 68 NifU-like domain containing proteins, including all sequences identified for apicomplexan parasites and two representative species from the plant, fungus, and animal kingdoms (see also Table S1 in File S1). Circles represent branch points with bootstrap values of 95–100% (black), 85–95% (dark gray), 70–85% (light gray), and 50–70% (white). Azotobacter vinelandii NifU was used as the outgroup. The mitochondrial “ISU” and “NFU1” clades (light gray shading) constitute of proteins involved in the ISC system and were well supported in all different analyses with bootstrap values of 100% in all cases for “ISU” and 52–78% for “NFU1”. The remaining “NFU” sequences, constituting members of the SUF system restricted to plants, algae, and apicomplexan species, group in clades with sequences from the same or related species, but do not consistently form a plastid “NFU” clade. The Plasmodium subclades are indicated by dashed lines. Note that the apicomplexan parasites of the genus Cryptosporidium that are known to lack an apicoplast and fully functional mitochondrion [44] lack both genes encoding NFU-like proteins.