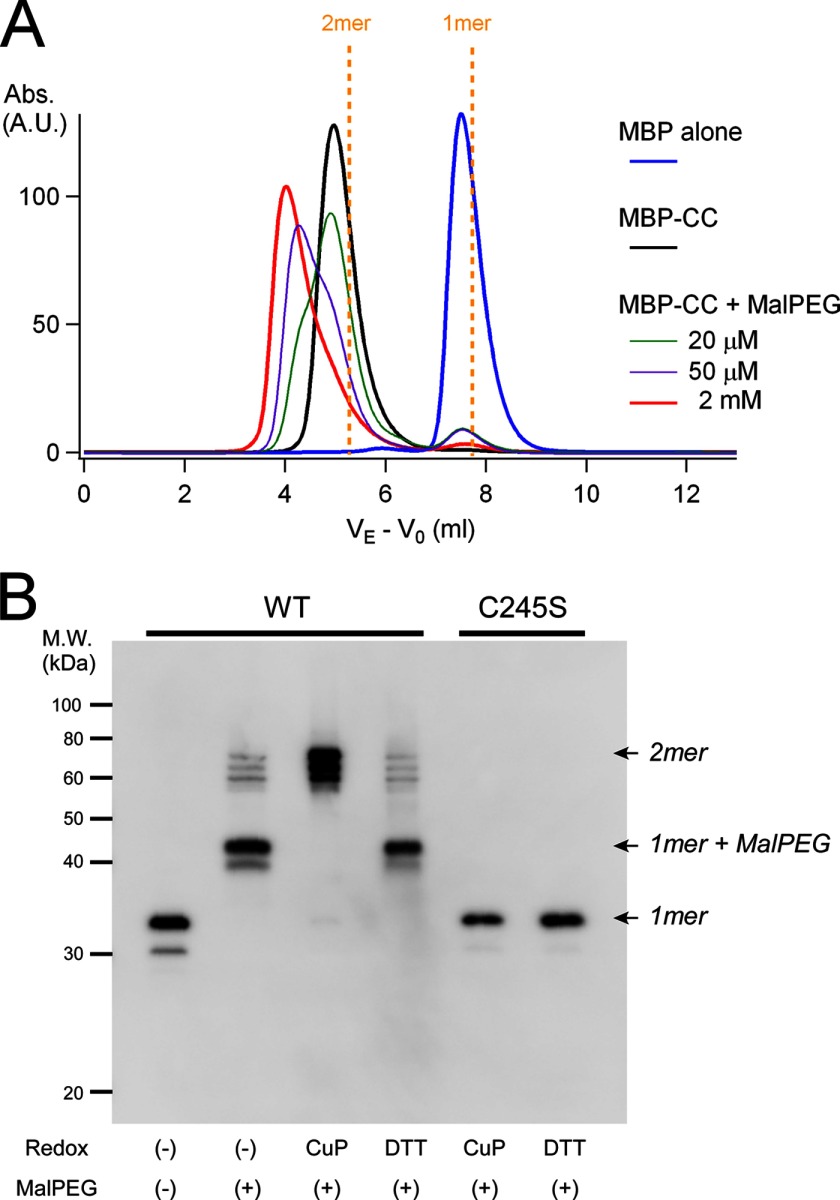
FIGURE 6.
Analysis of accessibility to Cys-245 under redox conditions. A, the chemical accessibility of maleimide to Cys-245 in the coiled-coil proteins was analyzed by size exclusion chromatography. Protein samples were mixed with various concentrations of MalPEG 10,000 (20 μm (green), 50 μm (purple), and 2 mm (red)) and incubated for 1 h at 4 °C prior to analysis. Signals were derived from the eluates for MBP (45 kDa), the MBP-tagged coiled-coil protein (MBP-CC; 51 kDa), and the MBP-tagged coiled-coil protein bound to MalPEG 10,000 (51 + n × 10 kDa (n = 1 or 2)). MalPEG itself did not show any signal, and MBP does not contain Cys. VE is corrected for void elution volume by subtracting that of blue dextran (V0). Dashed yellow lines indicate the predicted elution profiles of the MBP-tagged dimeric and monomeric coiled-coil proteins. A.U., absorbance units. B, maleimide accessibility to Cys-245 in the coiled-coil domain of full-length mVSOP/Hv1 WT and C245S mutant channels under redox conditions was analyzed by Western blotting. Redox conditions are indicated. CuP, copper phenanthroline.