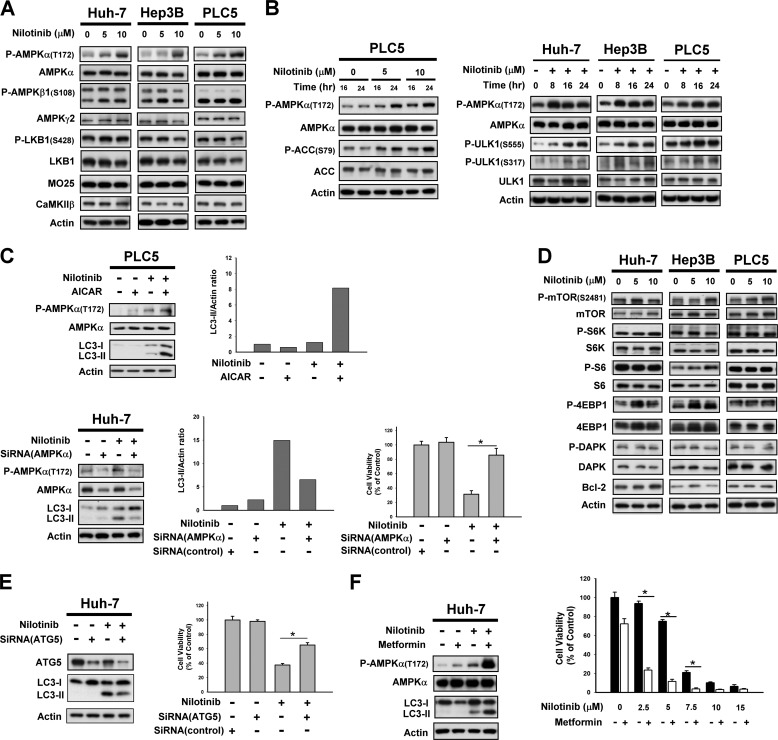
FIGURE 3.
AMPK mediated nilotinib-induced autophagy. A, target validation of CIP2A-Akt-4EBP1. A, dose-dependent analysis of AMPK-related molecules in HCC cells. Cells were exposed to nilotinib at the indicated concentrations for 24 h. B, time-dependent analysis of P-AMPKα, AMPKα, P-ACC, ACC, P-ULK1, and ULK1 in HCC cells. Cells were exposed to nilotinib at the indicated concentrations for 24 h. C, validation of AMPKα mediation of nilotinib-induced autophagy. Top, co-treatment with AICAR, an activator of AMPK, increased nilotinib-induced autophagy. Cells were treated with nilotinib (10 μm) and/or AICAR (1 mm) for 24 h. Bottom, silencing AMPKα by siRNA reduced nilotinib-induced autophagy and cell death. Huh-7cells were transfected with control or AMPKα siRNA for 48 h then treated with nilotinib (10 μm) for 24 h. Cell viability was measured by MTT assay. D, dose-dependent analysis of other autophagy-related molecules. Cells were exposed to nilotinib at the indicated concentrations for 24 h. E, silencing Atg 5 by siRNA reduced nilotinib-induced autophagy and cell death. Huh-7 cells were transfected with siRNA for 48 h then treated with nilotinib (10 μm) for 24 h. Cell viability was measured by MTT assay. F, adding metformin increased nilotinib-induced autophagy and cell death. Cells were exposed to nilotinib at 10 μm or at the indicated concentrations and/or metformin at 10 mm for 24 h.