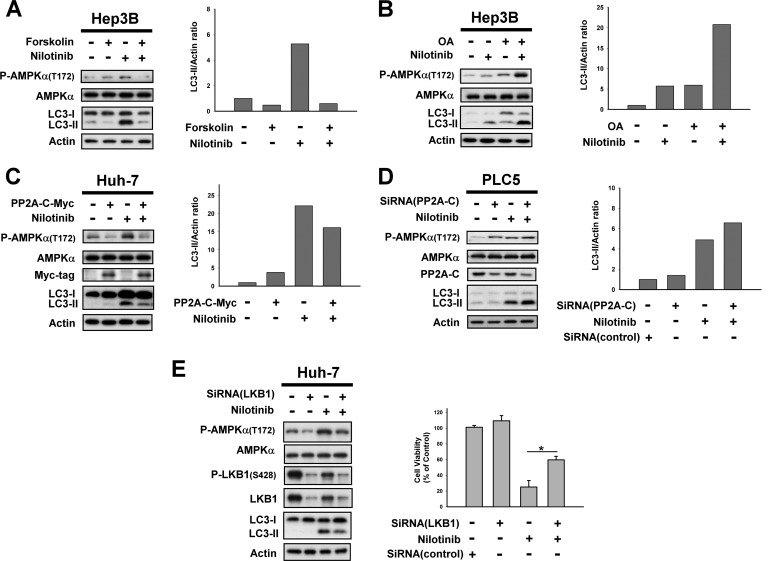
FIGURE 4.
PP2A mediates nilotinib-induced activation of AMPK. A, left, co-treatment with forskolin, a PP2A agonist, reverses the effect of nilotinib on P-AMPKα and autophagy. Right, immunoblots were scanned using a UVP BioSpectrum AC image system and quantitated using VisionWork LS software to determine the ratio of the level of LC3-II to actin. B, co-treatment with okadaic acid, a PP2A inhibitor, enhanced the effect of nilotinib on P-AMPKα and autophagy. C, ectopic expression of AMPKα abolishes effects of nilotinib on autophagy in Huh-7 cells. Cells were transfected with AMPKα-myc and were selected for 8 weeks by G-418. Analysis of autophagy was performed by Western blot (WB) after cells were sequentially exposed to DMSO or nilotinib (10 μm) for 24 h. D, knockdown of PP2A-C enhanced nilotinib-induced autophagy. PLC5 cells were transfected with control or AMPKα siRNA for 48 h and then treated with nilotinib (10 μm) for 24 h. E, silencing LKB1 by siRNA reduced nilotinib-induced autophagy. Huh-7 cells were transfected with control or LKB1 siRNA for 48 h then treated with nilotinib (10 μm) for 24 h. Cell viability was measured by MTT assay.