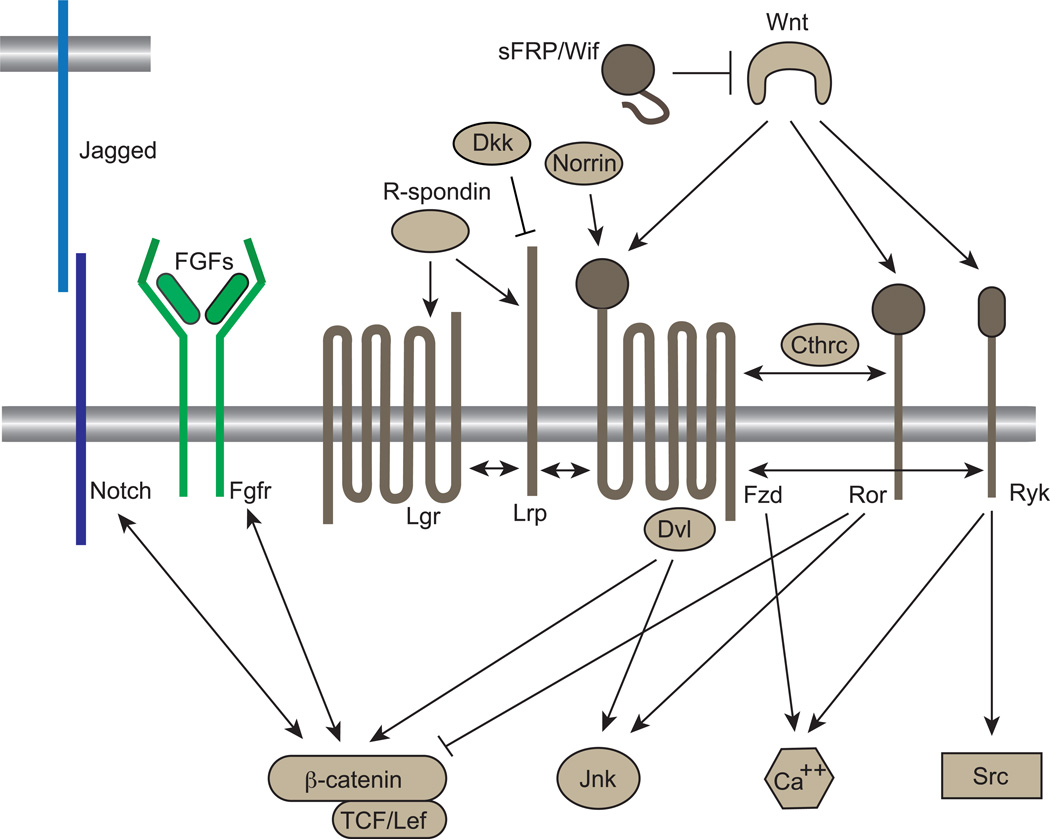
Figure 1.
Wnt signaling pathways. Canonical vs. non-canonical Wnt signaling is dependent on ligand, receptor and co-receptor interactions. Wnt ligands can activate both canonical pathways by binding to Fzd receptors and non-canonical pathways through co-receptors such as Ror and Ryk. Ror can inhibit β-catenin activity while activating Jnk. R-spondins directly bind to Lgr and Lrp co-receptors that interact with Fzd to stimulate/augment β-catenin signaling. Norrin can also activate the canonical pathway, independent of Wnts. Wnt Inhibitors such as sFRP/Wif also regulate Wnt signaling by sequestering Wnt ligands, while Dkk interacts with Lrp to inhibit Wnt signaling. The Notch and Fgfr signaling pathways have been found to act both, upstream and downstream of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Figure modified from [3].