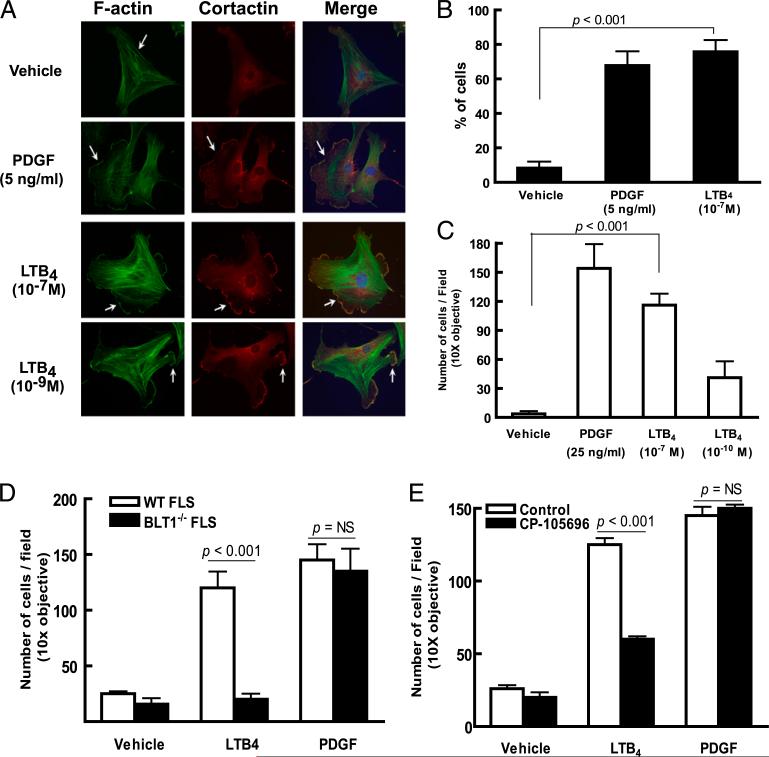
FIGURE 6.
LTB4 promotes synovial fibroblast migratory and invasive behavior. A, Lamellipodium formation in WT FLSs stimulated by LTB4. WT FLSs were plated on coverslips and stimulated and stained as labeled. Nuclei are visualized with a Hoechst dye (blue). Arrows indicate lamellopodia in FLSs stimulated by LTB4. Data are representative of three independent experiments. B, Percentage of FLSs demonstrating lamellipodium formation. The results represent the mean ± SEM of data pooled from three experiments. The p value was determined by the Student unpaired two-tailed t test. C, LTB4-induced invasion of FLSs. Primary FLSs placed in Matrigel-coated transwell dishes were stimulated as labeled and cells migrating to the lower membrane surface were enumerated. Results shown are the mean ± SEM of data pooled from four independent experiments. D, LTB4-induced invasion in FLSs requires BLT1 expression. WT or BLT1–/– FLSs were placed in Matrigel-coated transwells and stimulated and enumerated as in C. E, BLT1 antagonist CP-105,696 inhibits LTB4-driven FLS invasion. WT FLSs were pretreated with CP-105,696 for 30 min prior to measuring LTB4- or PDGF-driven invasion as in C. Data shown in D and E are the mean ± SEM of data pooled from three experiments. The p value was determined by the Student unpaired two-tailed t test.