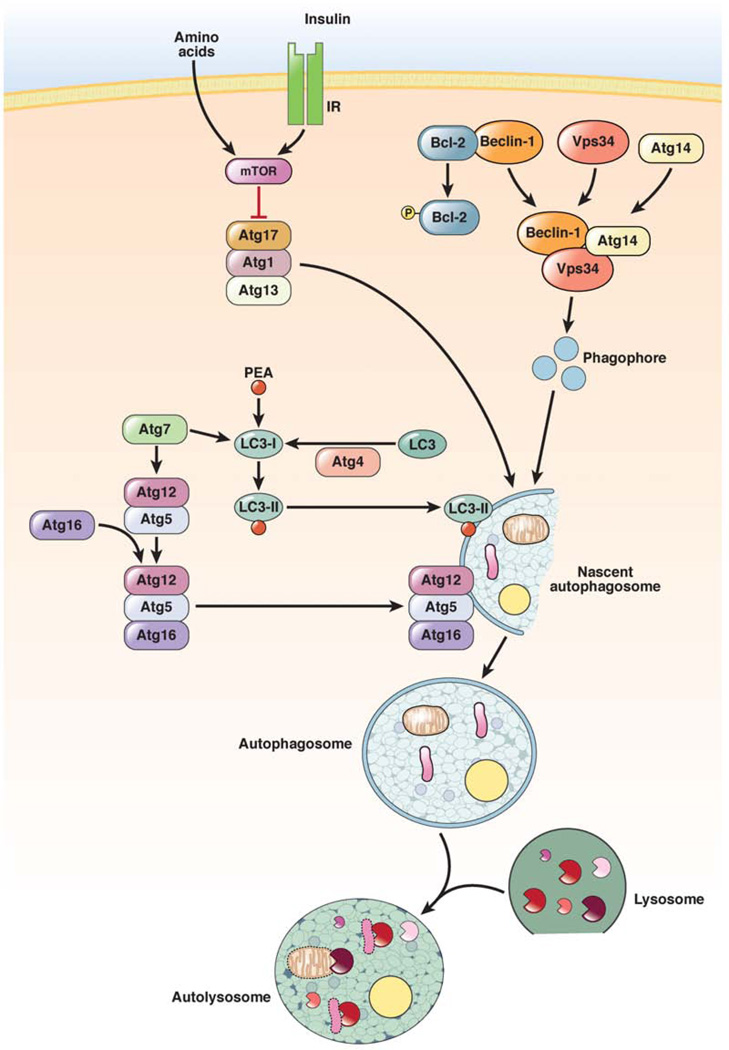
Figure 2.
Pathways that control levels of macroautophagy. Macroautophagy is regulated by 3 major pathways. The first is an inhibitory pathway in which nutrient or insulin stimulation of the mTOR signaling pathway blocks autophagosome formation (red line). Two other pathways are stimulatory. In one, phosphorylation of Bcl-2 dissociates it from beclin-1, which allows beclin-1 to form a complex with the PI3K Vps34 that produces phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate, which is required for induction of autophagy. The other pathway involves a series of conjugation steps that generate LC3-II and the Atg5–Atg12–Atg16 protein complex, which are both necessary for autophagosome formation. IR, insulin receptor; PEA, phosphatidylethanolamine.