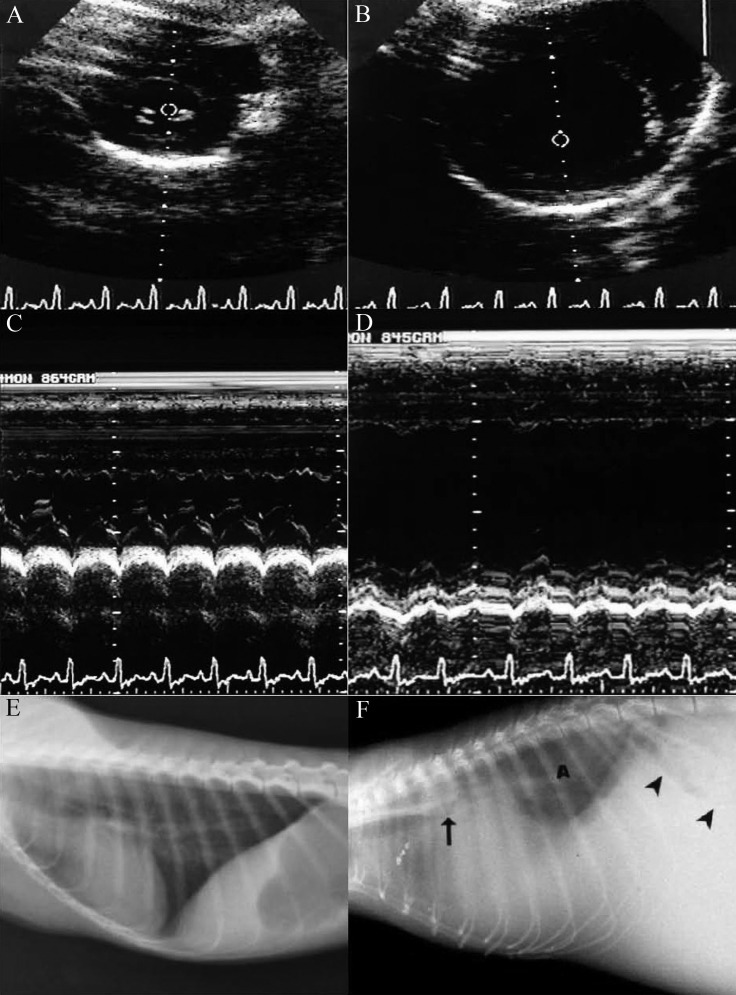
Figure 1.
A) 2-Dimensional echocardiogram image of left ventricle on cross-section at level of papillary muscles during end-diastole in a normal owl monkey. B) 2-Dimensional echocardiogram image of left ventricle on cross section at level of papillary muscles during end diastole in an owl monkey with marked myocardial hypertrophy and dilatation. C) M-mode echocardiogram image of left ventricle on cross section of the same normal animal. D) M-mode echocardiogram image of left ventricle on cross section of the same animal with marked hypertrophy and dilatation. Note the poor ventricular contraction. E) Lateral thoracic radiograph of a normal owl monkey. F) Lateral thoracic radiograph of the owl monkey depicted in panels B and D. Note the severe hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, with elevation of the carina (arrow) secondary to left heart enlargement. The heart and the diaphragm are obscured by extensive pleural effusion. Note the pulmonary radiodensity (marked A in the image) due to pulmonary edema, stomach with caudal shift to the axis (arrowheads) from hepatomegaly, and loss of abdominal detail from peritoneal fluid resulting in marked abdominal distention. This monkey had a vertebral heart score of 13.