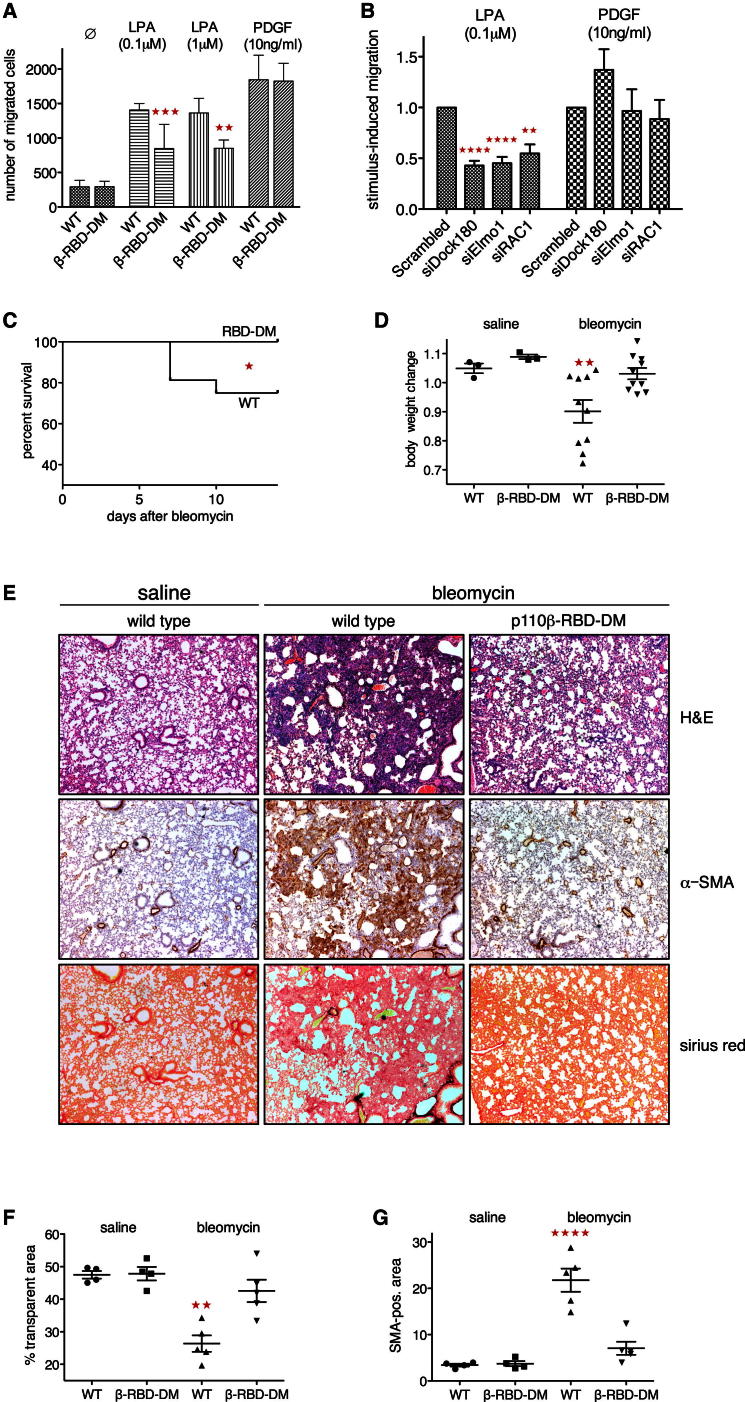
Figure 7.
p110β-RBD-DM Mice Are Protected from Bleomycin-Induced Lung Fibrosis
(A) p110β-RBD-DM fibroblasts show reduced migration in gradients of LPA. Migration of wild-type and p110β-RBD-DM MEFs in gradients of LPA and PDGF was assessed in transwell filter assays (n = 3; mean with SD; one-way ANOVA).
(B) Dock180, Elmo1, and RAC1 are required for fibroblast migration in gradients of LPA. Immortalized wild-type MEFs were transfected with scrambled duplex or gene-specific siRNA pools targeting Dock180, Elmo1, or RAC1. Migration in gradients of LPA and PDGF was assessed in transwell filter assays and cell numbers were normalized to control conditions (n = 4; mean with SEM; one-way ANOVA).
(C) p110β-RBD-DM mice are protected against death from bleomycin-induced lung damage. Wild-type and homozygous p110β-RBD-DM mice were treated with a single intratracheal dose of bleomycin (1.25 U/kg) and observed for 14 days (n = 16 mice per genotype; Mantel-Cox test).
(D) p110β-RBD-DM mice are protected against weight loss following bleomycin instillation. Wild-type and p110β-RBD-DM mice received a single intratracheal dose of saline (n = 3 per genotype) or bleomycin (n = 10 per genotype) and weights were taken 14 days later (mean ±SEM; one-way ANOVA).
(E) p110β-RBD-DM mice are protected from bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. Representative lung areas from wild-type and homozygous p110β-RBD-DM mice 14 days after treatment with intratracheal bleomycin (×4 magnification). Top: H&E; middle: IHC for α-SMA; bottom: Sirius red.
(F) p110β-RBD-DM mice are protected against loss of transparent lung areas following bleomycin instillation. Lungs were analyzed by H&E 14 days after bleomycin challenge. Multiple nonoverlapping areas of representative sections from each lung were photographed and transparent (white) areas were quantified using Nikon NIS elements software (mean ±SEM; one-way ANOVA; see Figure S7C for raw data).
(G) p110β-RBD-DM mice accumulate fewer activated lung fibroblasts following bleomycin instillation. Lungs were analyzed by immunohistochemistry for smooth muscle antigen (α-SMA) 14 days after bleomycin challenge. Multiple nonoverlapping areas of representative sections from each lung were photographed and SMA-positive (brown) areas were quantified using Nikon NIS elements software (mean ±SEM; one-way ANOVA; see Figure S7D for raw data).
See also Figure S7.