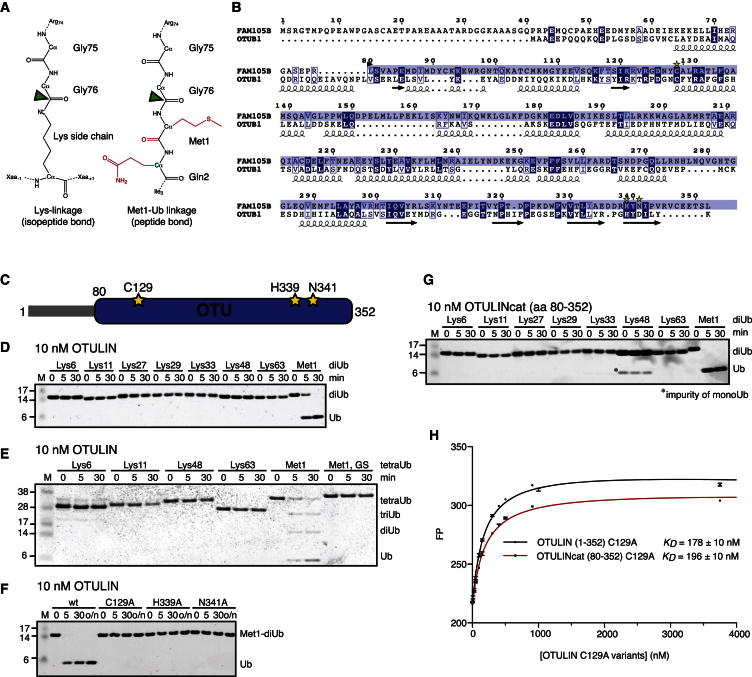
Figure 1.
Identification and Specificity of OTULIN
(A) Chemical difference between an isopeptide (left) and Met1-peptide linkage (right) in diUb. The distal Ub (top) is linked via its C-terminal Gly75-Gly76 sequence to a Lys side chain ε-amino group in another Ub or on a substrate, generating a branched peptide. In a Met1-linked chain, the C-terminal Gly76 is connected to Met1 of the distal Ub in a standard peptide linkage. The Met1 and Gln2 side chains, as well as the Met1 carbonyl (red), represent steric differences in comparison to an isopeptide linkage. A green arrow indicates the scissile bond in a DUB reaction.
(B) Sequence alignment of FAM105B/OTULIN with OTUB1. Sequence identity is 18% for the catalytic domain. Secondary structure elements are shown for OTUB1. The OTU domain is indicated in blue, and catalytic residues are labeled with yellow stars.
(C) The domain structure of OTULIN colored as in (B).
(D) Linkage specificity of OTULIN. diUb (1 μM) of all possible linkage types is hydrolyzed over a time course by 10 nM OTULIN and visualized on silver-stained 4%–12% gradient SDS-PAGE gels. See Figure S1D for the assay at 1 μM OTULIN concentration.
(E) Cleavage of tetraUb chains, as in (D). The last substrate is a Met1-tetraUb with G76S mutation in all Ub moieties.
(F) Hydrolysis of Met1-diUb by OTULIN wild-type (WT) and catalytic mutants as indicated.
(G) The OTU domain of OTULIN encodes Met1-linked Ub specificity. diUb specificity analysis as in (D) with OTULIN 80–352 at a 10 nM concentration.
(H) Affinity measurements by fluorescence anisotropy with OTULIN (1–352) C129A or OTULIN (80–352) C129A and FlAsH-tagged Met1-diUb, as described in the Extended Experimental Procedures. Error bars represent SD from the mean of measurements performed in triplicate.