Figure 3.
Substrate-Assisted Catalysis in OTULIN
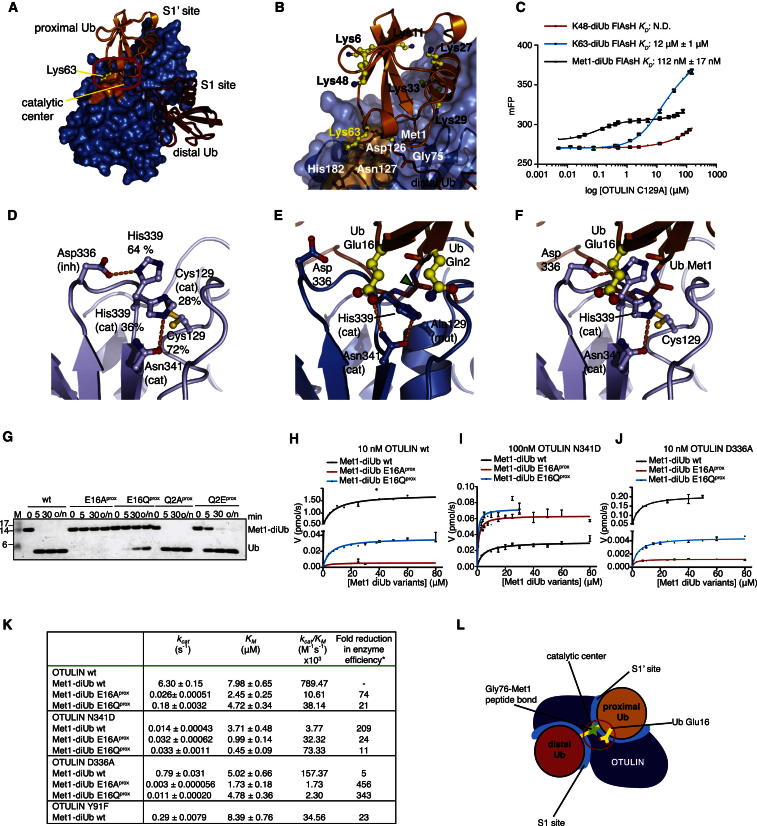
(A) The OTULIN-diUb complex is shown with OTULIN under a blue surface and Met1-diUb colored as red and orange for the distal and proximal moieties, respectively. The catalytic center and Lys63-binding pocket is shown boxed.
(B) A close-up view of (A) showing all Ub Lys residues on the proximal Ub (yellow). Lys63 and Met1 are spatially close.
(C) Affinity measurements of OTULIN C129A with K48-, K63, and Met1-diUb linkages performed with fluorescence anisotropy (Ye et al., 2011). Error bars represent SD from the mean of measurements performed in triplicate.
(D–F) A close-up image of the OTULIN catalytic center showing key residues. Dotted lines indicate hydrogen bonds.
(D) Unliganded OTULIN, shown as in Figure 2C.
(E) OTULIN C129A (blue) in complex with Met1-diUb (red and orange). Residues from the proximal Ub are shown in yellow. A green arrow indicates the scissile bond (compare to Figure 1A).
(F) Superposition of (D) with the Met1-diUb from (E). The carbonyl of Met1 and the side chain of Glu16 of the proximal Ub disengage the autoinhibition of His339. Gln2 is omitted for clarity.
(G) OTULIN hydrolysis of Met1-diUb mutated in the proximal moiety performed as in Figure 1D. o/n, overnight incubation.
(H–J) Kinetic parameters of OTULIN variants measured by fluorescence anisotropy. Initial rates of hydrolysis at varying substrate concentrations containing 150 nM FlAsH-tagged Met1-diUb variants were fitted to the Michaelis-Menten kinetic model with GraphPad Prism 5. Error bars represent SDs from the mean of measurements performed in triplicate.
(K) Summary of kinetic parameters measured. *, fold reduction in enzyme efficiency relative to OTULIN WT + Met1-diUb WT.
(L) A schematic representation of OTULIN mechanism, which involved extensive S1 and S1’ sites and substrate-assisted catalysis mediated by Ub Glu16.