Figure 5.
Importance of Ub Glu16 for Met1-polyUb Biology
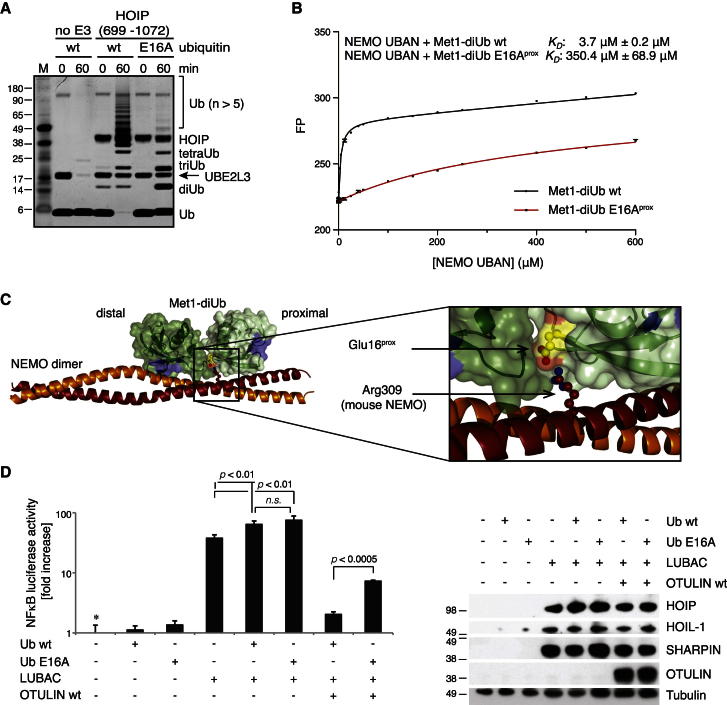
(A) A minimal HOIP construct (aa 699–1072) that efficiently assembles Met1-Ub chains with WT Ub (Smit et al., 2012; Stieglitz et al., 2012) is less efficient with Ub E16Aprox in vitro. A silver-stained SDS-PAGE gel is shown.
(B) Fluorescence anisotropy of NEMO UBAN domain binding to FlAsH-tagged Met1-diUb and Met1-diUb E16Aprox. The UBAN domain binds the mutant Ub chain with ∼100-fold lower affinity. Error bars represent SD from the mean from triplicate measurements.
(C) Structural basis for decreased affinity of NEMO for Met1-diUb E16Aprox mutant. The structure of the NEMO UBAN domain dimer (orange) bound to Met1-diUb is shown (PDB 2ZVN [Rahighi et al., 2009], one diUb omitted for clarity). Ub molecules are shown under a green surface with Ile44 hydrophobic patches in blue. Glu16 and its interacting residue Arg309 (mouse NEMO, corresponding human residue Arg312) are shown in stick representation. The inset highlights this interaction. Glu16prox also bridges the two Ub moieties and interacts with the C terminus of a distal Ub (data not shown).
(D) Luciferase assays performed as in Figure 4B for HEK 293ET cells transfected with or without LUBAC, WT OTULIN, and Ub WT or Ub E16A. p values are given to indicate significance. *, mean value set to 1; n.s., nonsignificant. Input levels of transfected proteins, analyzed by western blotting with the indicated antibodies, are shown on the right.