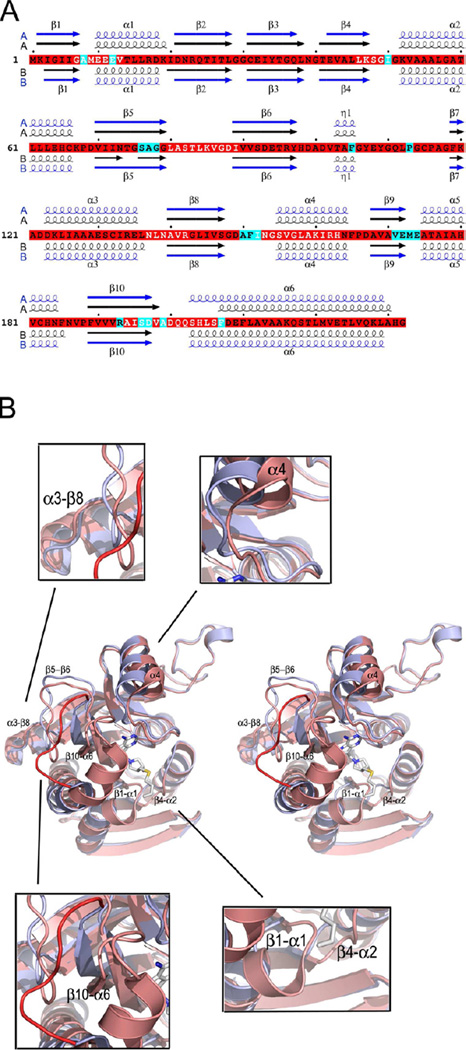
Figure 2.
Changes in the tertiary structure upon inhibitor binding. (A) The sequence of S. enterica MTAN (SeMTAN) and the alignment of secondary structures of inhibitor and adenine bound SeMTAN structures. The secondary structures in black are from Ade-SeMTAN crystal structure where monomer-A was in the open conformation and monomer-B with a bound adenine was in the closed conformation. The secondary structures shown in blue belong to BuT-DADMe-ImmA-SeMTAN structure. In the BuT-DADMe-ImmA-SeMTAN structure, both monomers were in the closed conformation and contained a bound inhibitor, BuT-DADMe-ImmA. The secondary structures of A-monomers and B-monomers are above and below the sequence, respectively. The residues highlighted in cyan are in contact with the inhibitor in the BuT-DADMe-ImmA-SeMTAN crystal structure. (B) Comparison of tertiary structures of the monomers in the open and closed conformation. The structure shown in light blue is the open conformation monomer-A of Ade-SeMTAN. The monomer colored in salmon shows ligand induced closed form. The bound inhibitor is BuT-DADMe-ImmA. The labeled regions move the most upon ligand binding; the same regions are shown with white letters in panel A. The red loop belongs to open conformation monomer and it indicates the site of the most change in the structure. See also Movie S1.