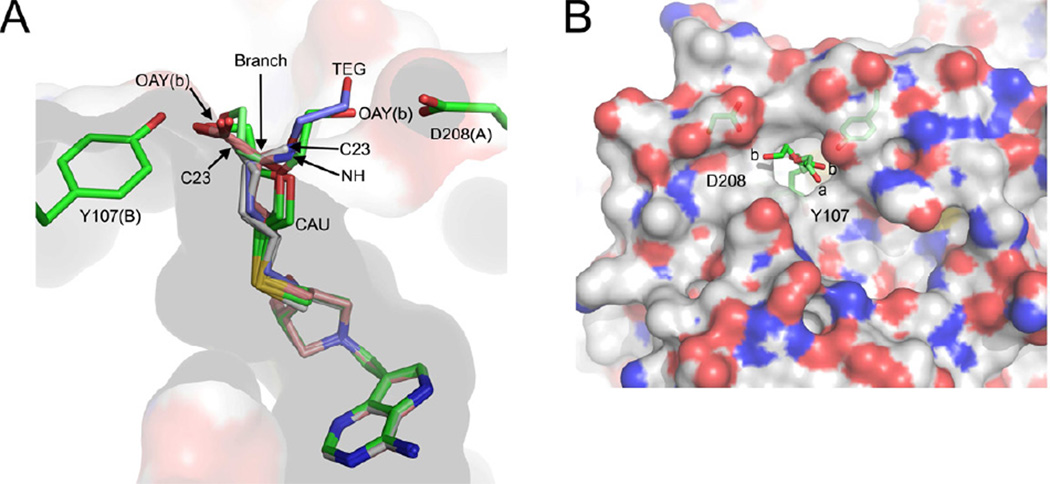
Figure 6.
Binding modes of transition state analogues with S. enterica MTAN (SeMTAN). (A) The binding pocket of monomer-A. The eight monomers of four SeMTAN dimers in complex with DADMe-ImmA based inhibitors as well as the adenine and triethylene glycol (TEG) bound monomer were superpositioned. The carbons of BuT-DADMe-ImmA, Homocys-DADMe-ImmA and DiEGT-DADMe-ImmA are colored in grey, salmon and green, respectively. The carbons of TEG are shown in light blue. MT-DADMe-ImmA is also included but is not visible in the figure. The longer inhibitors either face the Asp208 of the same monomer or Tyr107 of monomer-B; the site where the inhibitor molecule rotates either towards D208 or Y107 is indicated by an arrow and named branch point. The DiEGT-DADMe-ImmA of monomer-B of DiEGT-DADMe-ImmA-SeMTAN structure has two conformations where the oxygen [(OAY(b)] of DiEGT moiety is hydrogen bonded to Asp208 or Tyr107 (b stands for monomer-B). The C23 indicates the binding site of the carbon atom at the tip of the butylthio moiety of BuT-DADMe-ImmA. NH is the nitrogen atom of homocysteine of Homoc-DADMe-ImmA, and CAU is the carbon atom of the first ethyleneglycol repeat of diethyleneglycolthio moiety of DiEGT-DADMe-ImmA. (B) The two binding pocket extensions on the surface of SeMTAN in complex with DiEGT-DADMe-ImmA. The carbons, oxygens, nitrogens and sulfurs of the accessible surface area are shown in grey, red, blue and yellow, respectively. The binding modes of DiEGT moieties of monomer-A (a) and monomer-B (b) are shown. The oxygen labeled b is labeled as OAY(b) in panel A. The D208 and Y107 indicate putative binding site extensions that could be utilized by longer 5´-alkylthio substituted inhibitors. The figures were prepared with PyMOL