Figure 1.
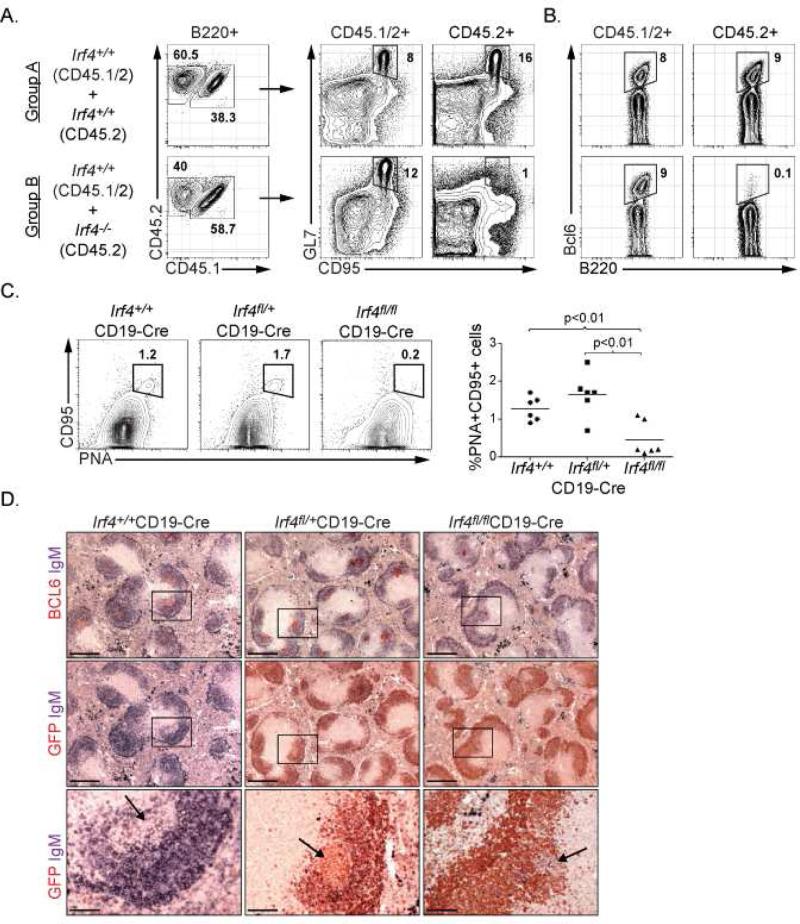
see also Figure S1. IRF4 regulates GC B cell differentiation. (A, B) 1:1 mixed bone marrow chimeras were generated such that the CD45.1 expressing compartments in Groups A and B were reconstituted with Irf4+/+ hematopoietic progenitors whereas the CD45.2 expressing compartments were reconstituted with Irf4+/+ and Irf4-/- hematopoietic progenitors, respectively. Reconstituted mice were immunized with SRBC and GC B cells were analyzed on Day 7 based on expression of GL7 and CD95 or intracellular Bcl6 expression after gating on CD45 polymorphic alleles and the B cell lineage marker B220 as indicated. Data are representative of two independent experiments using 5 mice per group. (C) Conditional deletion of Irf4 in B cells using CD19-Cre. Indicated mice were immunized with SRBC and splenic GC B cells were analyzed on Day 14 based on expression of PNA and CD95 after gating on B220. Each point in the right panel represents the numbers of GC B cells from individual mice. (D) Immunohistochemical analysis of GCs in mice described in (C). Splenic sections were stained for Bcl6, IgM and GFP as indicated.