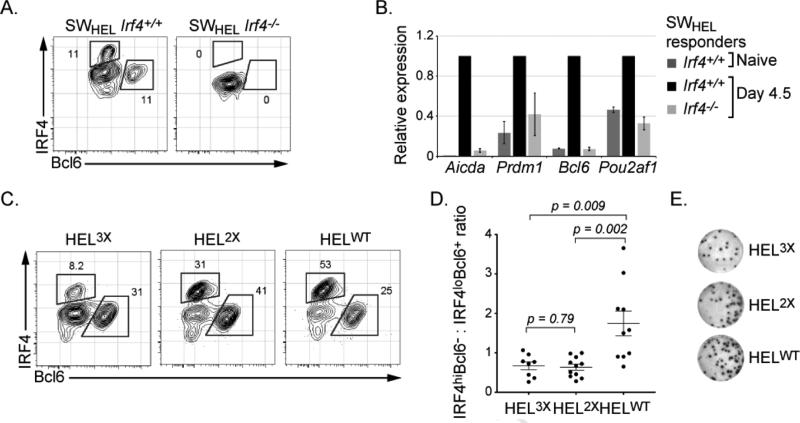
Figure 2.
see also Figure S2. IRF4 regulates GC B cell differentiation via the activation of the Bcl6 and Pou2af1 genes. Irf4+/+ or Irf4-/- SWHEL donor B cells were transplanted into CD45.1 hosts and immunized with HEL2XSRBC. (A) 4.5 days after immunization, donor derived antigen specific cells were identified based on B220+CD45.2+CD45.1- phenotype and binding to HEL antigen. Expression of IRF4 and Bcl6 expression was then analyzed by intracellular staining. (B) Cells described in (A) were sorted and RNA was analyzed by qRT-PCR. Indicated transcripts were normalized to those from Oct1 gene, the data represents the average ±SEM of three independent experiments with two mice per group. (C) Wild type SWHEL donor B cells were adoptively transferred into CD45.1 hosts and immunized with indicated HEL variants conjugated to SRBC. 4.5 days after immunization, donor derived antigen specific cells were identified and analyzed as in (A). (D) Quantitative analysis of experiments described in (C). The ratio of HEL-specific IRF4hiBcl6- to IRF4loBcl6+ expressing cells for individual mice is plotted from 3 independent experiments. (E) ELISpot analysis of HEL-specific IgG secreting PC cells from experiments in (C), representative results are shown, see Fig. S2 for quantitation.