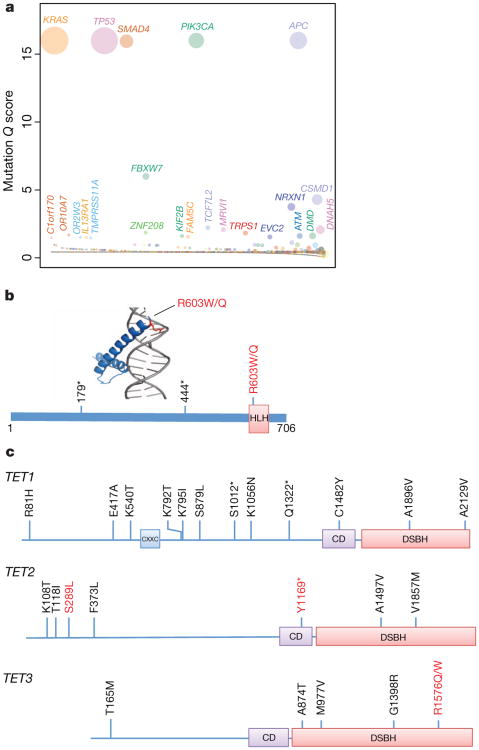
Figure 2. Significantly mutated colon cancer genes.
a, Genes evaluated for significance using Q score criteria for MSS samples are shown. Each circle represents a gene and the size of the circle is proportional to the mutation count for that gene. The genes are represented in order of increasing number of expected mutations from left to right on the x axis. Genes with a statistically significant Q score are labelled. b, TCF12 helix–loop–helix (HLH) domain structure bound to DNA showing the Arg603 hotspot and a schematic diagram depicting the various TCF12 mutations identified in this study. c, Somatic mutations in the TET gene family including TET1, TET2 and TET3 shown on the domain architecture of the TET genes. Recurrent mutations found in this study for TET3 and for TET2 by comparison to COSMIC data are shown in red. CD, Cysteine-rich domain; CXXC, Cys-X-X-Cys-type domain; DSBH, double-stranded β-helix 2OG-Fe(II)-dependent dioxygenase domain. Asterisks in b and c denote nonsense mutations that result in premature stop codons.