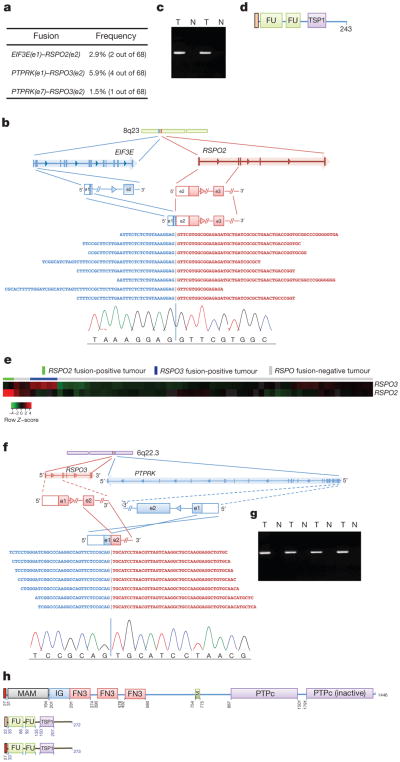
Figure 3. Recurrent R-spondin gene fusions.
a, List of type and frequency of R-spondin gene fusions in colon cancer. b, Cartoon depicting the location, orientation and exon–intron architecture of EIF3E–RSPO2 fusion on the genome. The read evidence for the EIF3E(e1)–RSPO2(e2) fusion identified using RNA-seq data is shown. c, Independent reverse transcriptase (RT)–PCR-derived products confirming the EIF3E(e1)–RSPO2(e2) somatic fusion resolved on an agarose gel. The RT–PCR product was Sanger-sequenced confirming the fusion junction and a representative chromatogram is shown in b. d, Schematic of the resulting EIF3E(e1)–RSPO2(e2) fusion protein. e, Tumours harbouring R-spondin fusions show elevated expression of the corresponding RSPO gene as depicted by the heat-map. f, Cartoon depicting the location, orientation and exon–intron architecture of the PTPRK–RSPO3 gene fusion on the genome. The read evidence for PTPRK(e1)–RSPO3(e2) fusion identified using RNA-seq data is shown. g, Independent RT–PCR-derived products confirming the PTPRK(e1)–RSPO3(e2) somatic fusion resolved on an agarose gel. The RT– PCR product was Sanger-sequenced confirming the fusion junction, and a representative chromatogram is show in panel f. h, Schematic of PTPRK, RSPO3 and the resulting PTPRK(e1)–RSPO3(e2) fusion proteins. FN3, fibronectin type 3 domain; FU, furin-like repeats; IG, immunoglobulin; MAM, meprin A5 receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase mu domain; N, normal; PTPc, protein tyrosine phosphatase catalytic domain; T, tumour; TM, transmembrane domain; TSP1, thrombospondin type 1 repeats.