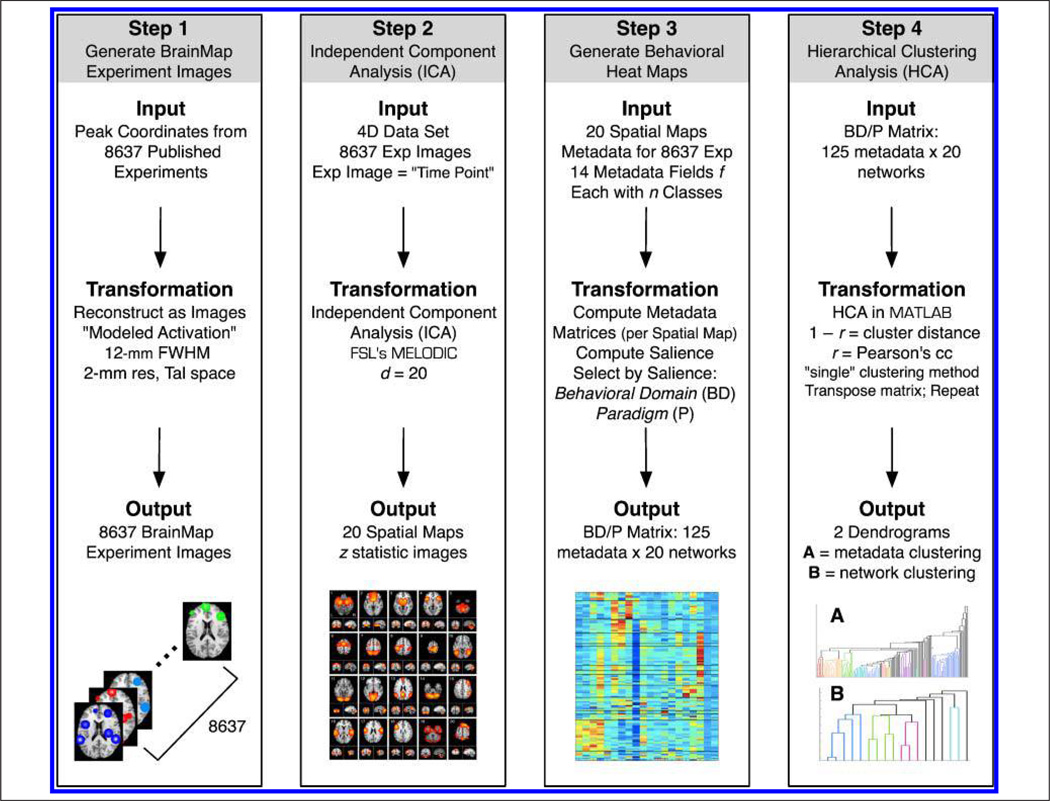
Figure 1.
The data processing pipeline included four steps. Step 1: Peak coordinates in BrainMap were smoothed (12 mm FWHM) to generate 8637 modeled activation images. Step 2: ICA was applied to this 4D data using FSL’s MELODIC to decompose the experiment images into 20 spatially independent components. Step 3: The matrix that quantifies the relationship between components and BrainMap experiments was utilized to compute a set of matrices that corresponded to 14 independent metadata fields, each with n classes. The relative salience as computed for each field and the two fields with the highest salience were selected for further analysis: behavioral domain and paradigm. Step 4: HCA was performed on the concatenated behavioral domain and paradigm matrix (125 metadata classes × 20 networks). Clustering was first performed on the combined matrix to determine groupings across metadata classes; subsequently, the matrix was transposed and the analysis repeated to quantify similarity across networks.