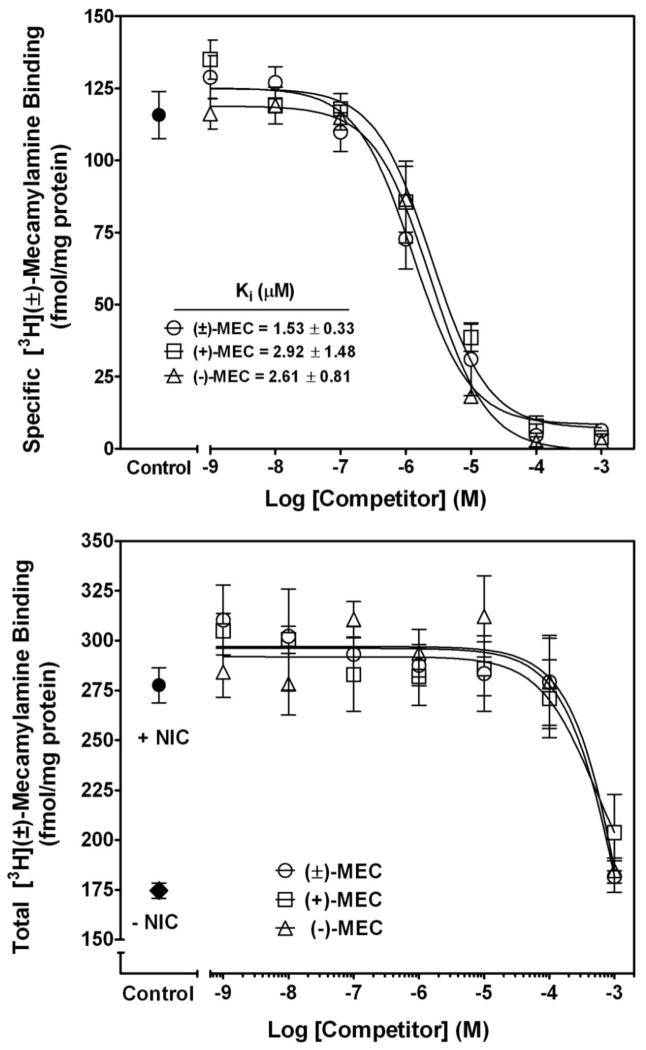
Fig. 5. High concentrations of mecamylamine stereoisomers are required to compete for racemic [3H]-mecamylamine binding to rat brain membranes in the presence of 1 mM S(−)nicotine.
Competitive binding assays were performed for racemic, S(+)- and R(−)-mecamylamine (1 nM - 1 mM) against 100 nM racemic [3H]-mecamylamine both in the absence (top) and presence of nicotine (1mM; bottom panel). Nonspecific binding was determined using 100 μM racemic mecamylamine. Data are expressed as fmol/mg protein and represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Curves were generated by nonlinear regression using a one-site model. Ki values are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. Ki values could not be calculated in the presence of nicotine.