Fig. 6.
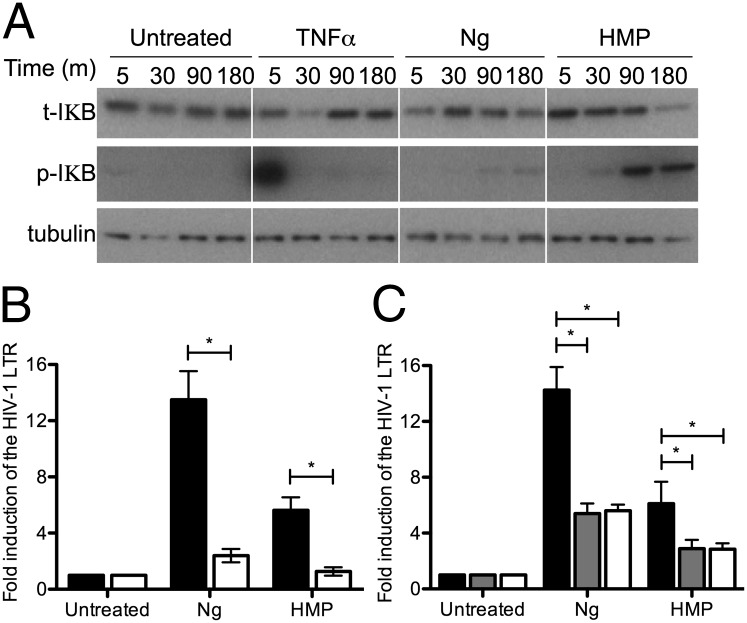
Activation of HIV-1 expression by HMP requires NF-κB. (A) Phosphorylation and degradation of cytoplasmic IκB in response to HMP. A3.01 cells were treated with 10 ng/mL TNF-α or 20 μg/mL HMP or were infected with an MOI = 10 of Ng. Whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted with antibodies directed against IκBα (t-IκB) and its phosphorylated form (p-IκB); α/β tubulin was used as a loading control. (B) Effect of the proteosome inhibitor, MG-132 on HIV-1 LTR induction by Ng and HMP. Jurkat 1G5 cells were preincubated with 0 nM (black bars) or 250 nM (white bars) MG-132 before infection with MOI = 10 of Ng or 25 μg/mL of HMP, and HIV-1 LTR expression was quantified by luciferase assay. Data represent the fold induction of expression over untreated cells. Data are the mean of five independent experiments ± SEM. *P < 0.05; ANOVA, Bonferroni. (C) Effect of RNAi of NFKB1 and RelA on HIV-1 induction by Ng and HMP. Jurkat 1G5 cells were transfected with scramble shRNA (black bars) as a control or with shRNAs targeting NFKB1 (gray bars) or RelA (white bars). Cells were infected with a MOI = 10 of Ng or were treated with 20 μg/mL of HMP and HIV-1 LTR expression was quantified by luciferase assay. Data the mean of three independent experiments ± SEM. *P < 0.05; ANOVA, Bonferroni.