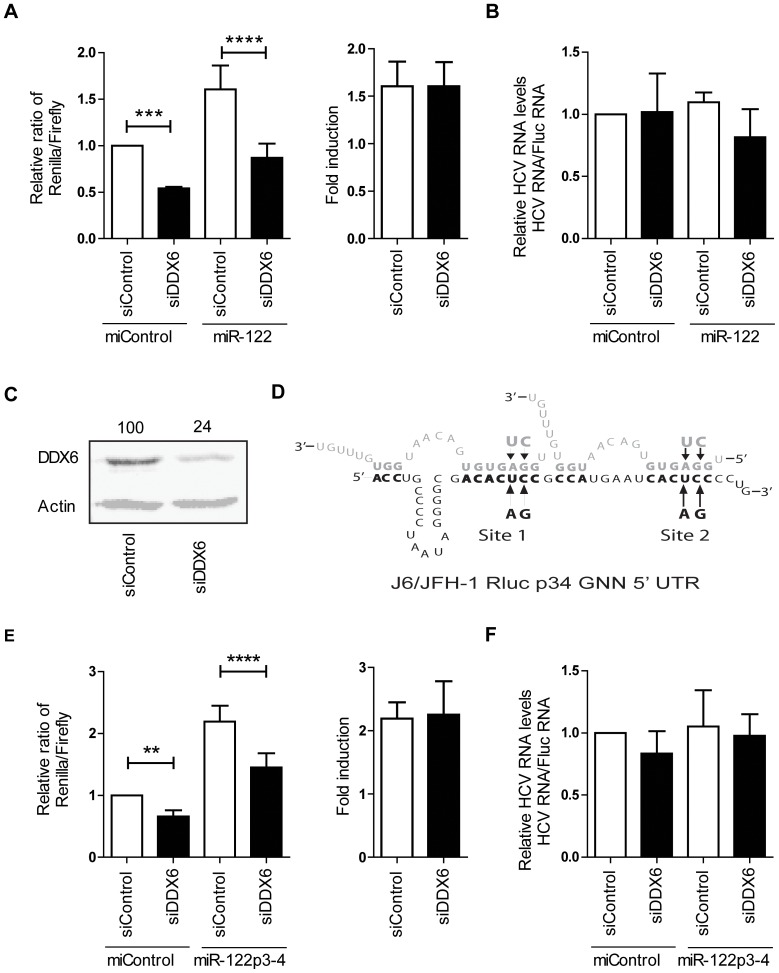
Figure 3. siDDX6 depletion decreases HCV translation, but does not affect miR-122 stimulation of HCV translation.
(A) Relative Rluc:Fluc expression in Huh7.5 cells co-electroporated with full-length, replication defective (J6/JFH-1 Rluc GNN) HCV RNA containing a Rluc reporter, a capped Fluc mRNA, and the indicated siRNA and miRNA. The graph on the right shows the relative fold translation stimulation by miR-122. (B) Relative RNA ratios of J6/JFH-1 Rluc GNN to capped firefly mRNA measured by qRT-PCR. (C) Western blot analysis show that siDDX6 depletes cells of DDX6 protein compared to siControl. (D) A schematic drawing of the 5′ UTR of J6/JFH-1 Rluc GNN RNA showing wild-type and mutant miR-122 binding sites (J6/JFH-1 Rluc GNN p34) and annealing pattern with the corresponding miRNA miR-122, or miR-122p34. (E) Relative Rluc:Fluc expression from J6/JFH-1 Rluc GNN p34 RNA co-transfected with capped Fluc mRNA, and the indicated siRNA and miRNA. The graph on the right shows the relative fold translation stimulation by miR-122p34. (F) Relative RNA ratios of J6/JFH-1 Rluc GNN p34 to capped firefly mRNA measured by qRT-PCR. Data in (A) represents the average of 5 independent experiments and the data in (C) represents the average of 8 independent experiments. Significance was determined by performing a one-way ANOVA with Bonferonni's Multiple Comparison Test.