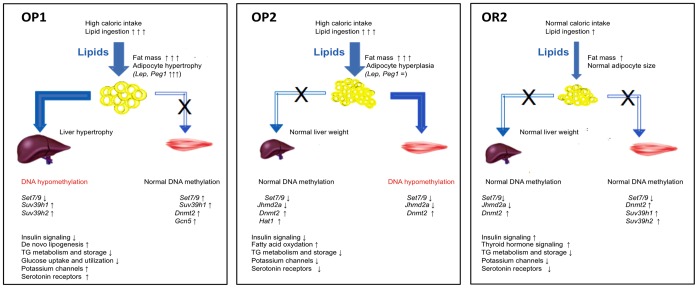
Figure 5. Schematic diagram summarizing the transcriptional data obtained for the liver, muscle and adipose tissue and the results of epigenetic studies in OP1, OP2 and OR2 mice.
Blue arrows represent potential lipid fluxes. In the hyperphagic OP1 and OP2 mice, lipid ingestion was much greater than in OR2 mice, in which caloric intake was normalized. In OP mice, excess lipids were initially stored in the adipose tissue, leading to adipocyte hypertrophy in OP1 mice and hyperplasia in OP2 mice, as a function of the level of expression of Lep and Peg1. In OR2 mice, lipids were stored in the adipose tissue without adipocyte abnormalities or ectopic storage, as in mice supplied with limited amounts of lipid. In OP1 mice, the excess lipids were stored in the liver, contributing to hepatic hypertrophy. Transcriptomic data indicated that de novo lipogenesis was activated in OP1 mice and that insulin signaling was greatly disturbed. In OP2 mice, genes related to insulin signaling were less affected, whereas genes involved in fatty acid oxidation were globally upregulated. Changes to hepatic metabolism, together with the probable redirection of lipids to muscle thus spared the liver from lipid accumulation. Finally, in OR2 mice, lipid metabolism as a whole was downregulated, whereas thyroid hormone signaling was upregulated. The HFD response was also associated, in OP1 mice, with an upregulation of potassium channels and serotonin receptors, subsequently reversed in both OP2 and OR2 mice. Changes in DNA methylation were observed in the livers of OP1 mice and the muscle of OP2 mice. In the liver, Set7/9 expression was decreased by the HFD in mice born to either lean or obese/diabetic mothers (F1LM and F2OM), whether OP or OR. In the livers of OP1 mice, DNA hypomethylation was associated with an upregulation of Suv39h1 and Suv39h2 expression, whereas, in both OR2 and OP2 mice, normal DNA methylation was associated with a decrease in Jhdm2a expression and an increase in the level of Dnmt2 mRNA. In muscle, normal DNA methylation was associated with an upregulation of Suv39h1, Set7/9 and Dnmt2 in OP1 and OR2 mice, contrasting with the lower level of expression of the Set7/9 and Dnmt2 genes in the muscle of OP2 mice presenting DNA hypomethylation.