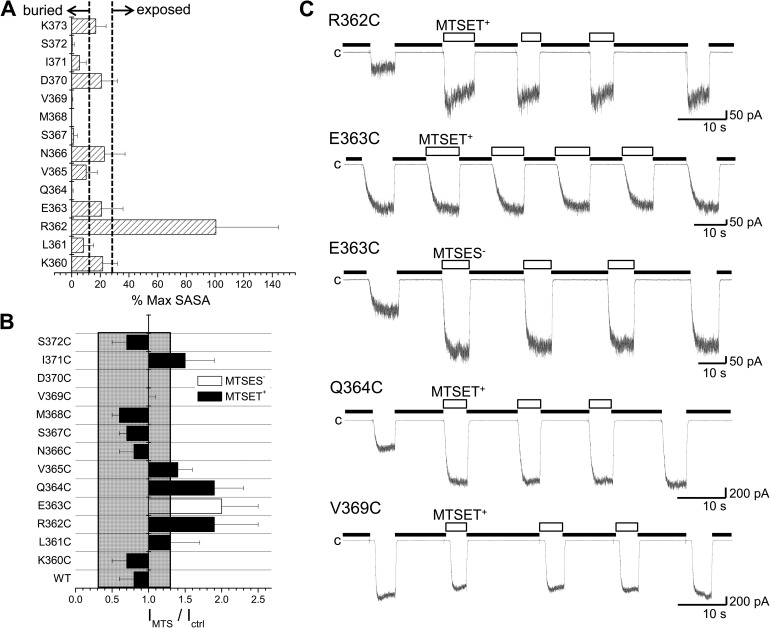
Figure 3.
SCAM of the CaM N-lobe–CaMBD2B complex. (A) Percentage of the maximum SASA computed for each residue of the CaMBD2B remaining accessible to solvent after formation of the KCa3.1–CaM complex, as illustrated in Fig. 1. The maximum SASA was taken as the SASA value obtained for a single KCa3.1 subunit in the absence of CaM. Dotted lines indicate areas referring to exposed residues with >30% of their maximum SASA remaining accessible to solvent and buried residues with <10% of their maximum SASA accessible to solvent. Buried residues include Q364, S367, M368, V369, I371, and S372, whereas R362 was confirmed as being the most solvent-exposed residue within the CaMBD2B. Values were obtained from MD trajectories spanning a total of 10 ns. The standard deviations in this case reflect the degree of structural variations during 10-ns simulations. (B) Accessibility of Cys engineered along the CaMBD2B segment to either 1 mM MTSET+ or 1 mM MTSES−. MTS reagents were applied internally according to the pulse application protocol illustrated in C. The ratio IMTS/Ictrl was taken as the ratio of the current amplitude for the Ca2+ pulse after MTS washout over the current amplitude obtained for the Ca2+ pulse before MTS application. Important changes were seen with the R362C, E363C, and Q364C mutants despite the fact that Q364C was predicted to be buried inside the CaM N-lobe–KCa3.1 complex and thus unlikely to be available for MTSET+ binding. The most important changes were seen with residue R362, which is highly solvent accessible. Values not included in the filled area refer to IMTS/Ictrl for which P < 0.005 relative to WT (IMTS/Ictrl (WT) ± 2.5 SD). (C) Examples of inside-out current recordings illustrating the action of MTS reagents on the R362C, E363C, Q364C, and V369C mutant channels. Experiments were performed in symmetrical 200-mM K2SO4 solutions with 25 µM of internal Ca2+ at a pipette potential of 60 mV on channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Label “c” refers to zero current measured in Ca2+-free conditions (thick line). Open boxes correspond to perfusion with a Ca2+ (25 µM) plus MTS reagent–containing solution (1 mM). Bars, 50 pA (R362C and E363C) or 200 pA (Q364C and V369C) and 10 s.