Fig. 4.
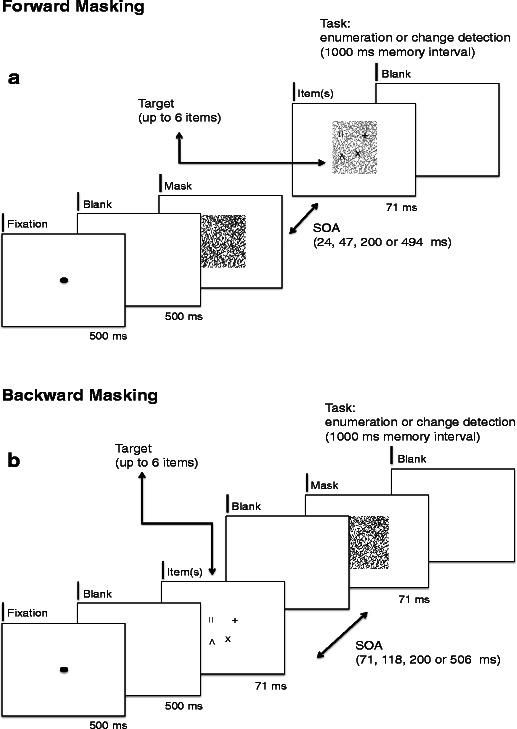
A single trial apiece in the forward-masking (panel A) and backward-masking (panel B) conditions. (A) Illustration of one trial in the forward-masking conditions. Throughout the trials, the two independent factors Target Set Size (1, 2, 3, 4, or 6, for enumeration; 2, 4, or 6, for change detection) and Mask–Target SOA (24, 47, 200, or 494 ms) were varied. The targets superimposed on the masking pattern (here shown 60 % transparent for illustrative reasons) were always presented for 71 ms, followed by a blank screen until the subject’s response in the enumeration condition. During change detection, a memory interval of 1,000 ms followed the target display, followed by a probe item for 71 ms. (B) Illustration of one trial in the backward-masking conditions. Throughout the trials, the two independent factors Target Set Size (1, 2, 3, 4, or 6, for enumeration; 2, 4, or 6, for change detection) and Mask–Target SOA (71, 118, 200, or 506 ms) were varied. The targets were always presented for 71 ms, followed (in the case of SOAs bigger than 71 ms) by a blank screen and a mask for 71 ms. In the enumeration condition, a blank screen followed until the subject’s response. During change detection, a memory interval of 1,000 ms followed the target display, followed by a probe item for 71 ms
