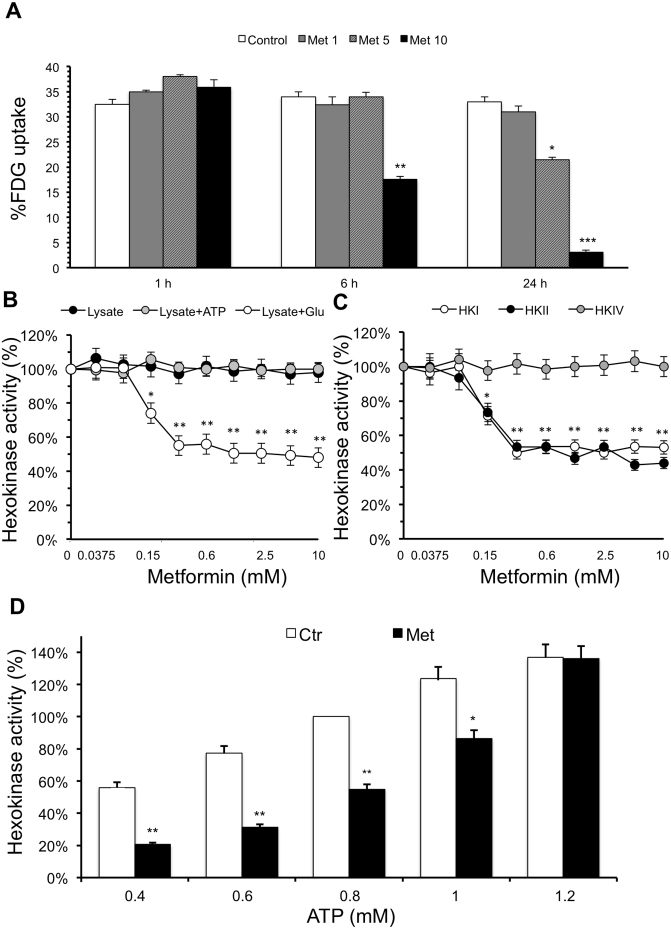
Figure 1. Effect of metformin on Calu-1 cells glucose consumption and HKs activity.
(A) Cell uptake of FDG was expressed as percentage of total tracer availability according to different metformin concentrations and exposure times. 1 mM metformin did not produce any significant modification, while tracer uptake decreased after 24 hrs exposure to metformin 5 mM. Highest drug concentration (10 mM) caused a significant reduction and virtually abolished glucose consumption at 6 and 24 hr. p values are shown for each comparison that was performed by one way analysis of variance. (B) Calu-1 HKs activity (expressed as percentage of control) is represented as function of metformin concentrations. The reaction was switched on after 10 minutes of metformin pre-incubation with Calu-1 total cell lysate (Lysate) or plus ATP 0.8 mM (Lysate + ATP) or Glucose 100 mM (Lysate + Glu). The reaction was switched on by adding to the solution respectively ATP + Glu (Lysate), Glucose (Lysate + ATP) and ATP (Lysate + Glu). Pre-incubation with metformin and glucose (Lysate + Glu) caused an inhibition of the HK I and II enzymatic activity that was dependent upon metformin concentration. This finding was not observed when the enzymes were pre-exposed to metformin alone (Lysate) nor to metformin and ATP (Lysate + ATP). (C) Enzymatic activity (expressed as percentage of control) of human purified HK I, HK II and HK IV observed after pre-incubation with glucose and different metformin concentrations. The reaction was switched on after 10 minutes by adding to the solution 0.8 mM ATP. Metformin induced a dose-dependent inhibition of catalytic activity of HK I and HK II. By contrast, it did not affect enzymatic activity of HK IV. (D) Dose dependent interference of ATP on human purified HK II inhibition caused by metformin. Phosphorylation rate is expressed as percentage of HKs activity measured after ten minutes pre incubation with glucose (100 mM) and different metformin concentrations and starting the reaction with ATP (0.4–1.2 mM). ATP 0.8 mM, was considered as reference value. Starting the reaction with ATP concentrations ≥1.2 mM fully abolished metformin effect. On the contrary, ATP levels below 1.2 mM reduced the extent of metformin inhibitory action in a dose dependent fashion. * = p < 0.05; ** = p < 0.01:*** = p < 0.001. Error bars indicate standard error.