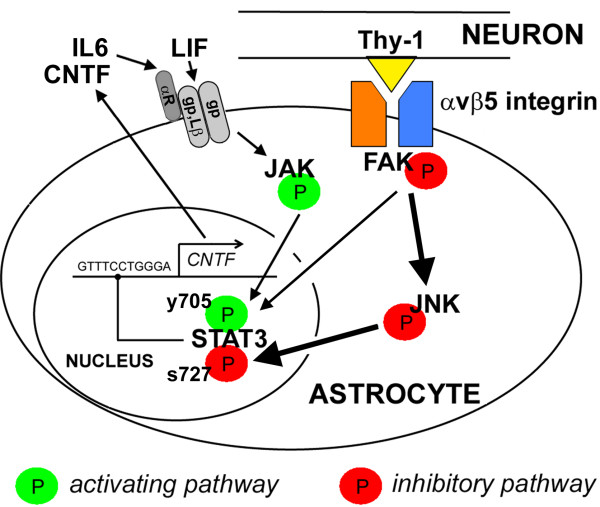
Figure 7.
Schematic representation of the proposed pathways that regulate astroglial CNTF. This study identifies an inhibitory pathway (Red) where ligands such neuronal Thy-1 bind to astrocyte αvβ5 integrin resulting in FAK phosphorylation. Subsequently, JNK is activated and phosphorylates STAT3 at an inhibitory serine-727 (s727) residue potently repressing transcription of CNTF. Conversely, the CNTF-stimulatory pathway is activated by neural cytokines such as CNTF, LIF and IL-6 which bind to their respective gp130 (gp) receptor complexes (CNTF: CNTFαR/LIFβR/gp130; LIF: LIFβR/gp130; IL-6: IL-6αR/gp130/gp130; Lβ indicates LIFβR), triggering recruitment of JAK to activate STAT3 by phosphorylation at the pro-transcription residue tyrosine-705, y705; Green). CNTF is known to activate STAT3 in astrocytes in vitro [9,87-90] and in vivo [91]. FAK may simultaneously stimulate the activating pathway, potentially representing another component of the tightly regulated CNTF gene expression under physiological conditions.