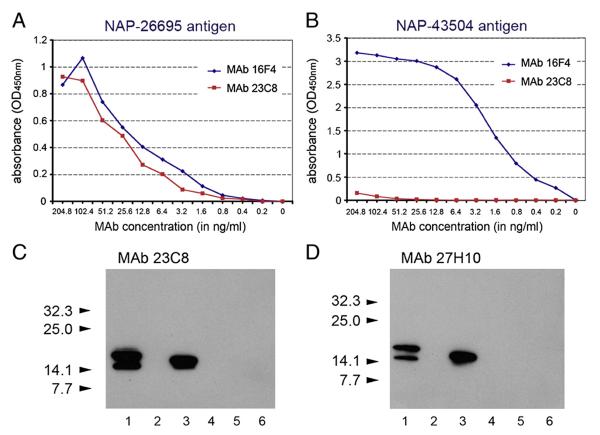
Fig. 1.
Characterization of MAbs against NAP-97–119 peptide. Comparison of NAP-97–119-specific MAb 23C8 and MAb 16F4 reactivity against NAP-26695 (A) and NAP-43504 (B) antigens in antigen-mediated ELISA. Purified MAbs with known protein concentration were incubated in 2-fold serial dilutions with the antigen. Results are presented as absorbance (OD450 nm). Both NAP-97–119-specific MAbs clone 23C8 and clone 27H10 reacted in immunoblotting (C and D) with homologous secretory NAP (H. pylori strain 26695) antigen from MV-s-NAP-infected Vero cells (lane 1) and E. coli expressed recombinant NAP-26695 antigen (lane 3) but not with non-homologous NAP-43504 recombinant antigen (lane 4). MV-GFP-infected Vero cells (lane 2) or protein extracts from E. coli BL21 Star (DE3) cells transformed with pET-28 empty expression plasmid were used as controls (lanes 5 and 6). Arrows indicate MW and position the pre-stained protein standards (C and D).