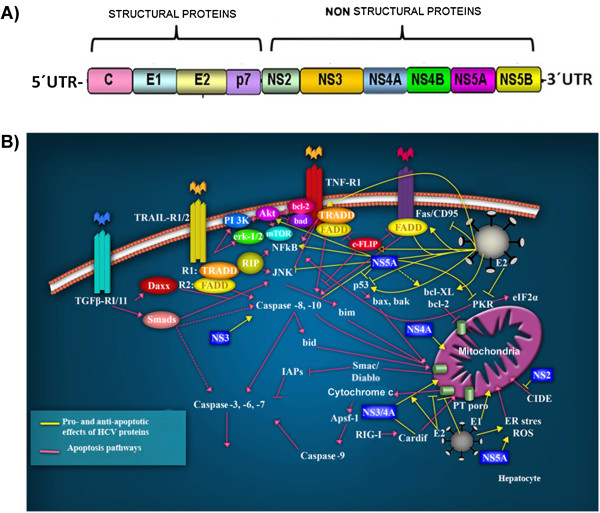
Figure 3.
The Hepatitis C virus and apoptotic signaling pathways. A) The Hepatitis C virus genome. A single open reading frame encodes four structural proteins and six nonstructural proteins. B) HCV-infected hepatocytes are recognized by the immune cells, that promote apoptosis via the death receptor ligands, TRAIL, TNFα, CD95 ligand, and TGF-β, as well as granzyme B/perforin (Pink lines). Ligand-induced apoptosis activates caspase-8, whereas activation of caspase-9 occurs via the mitochondrial permeability transition (PT) pore, triggering the activation of caspases cascade and the irreversible induction of apoptosis. For virtually all HCV proteins, pro- and anti-apoptotic effects have been described (Yellow lines). The structural (core C, E1 and E2) and nonstructural (NS2, NS3, NS4A and NS5A) proteins participate in the extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways. Modified from Fischer R. et al. (2007) [92].