Abstract
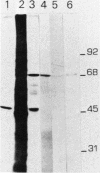
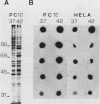
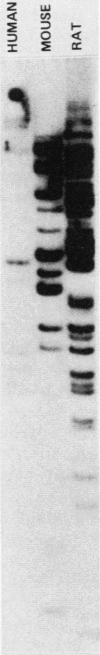
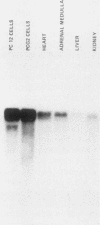
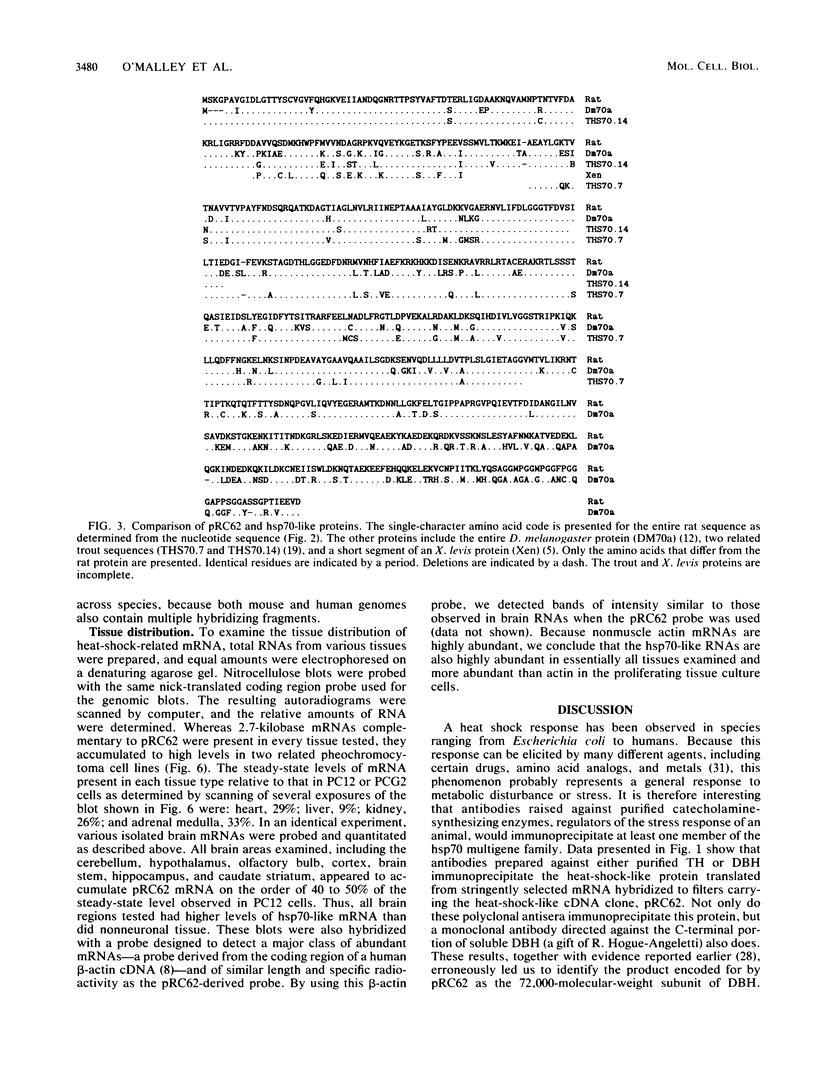
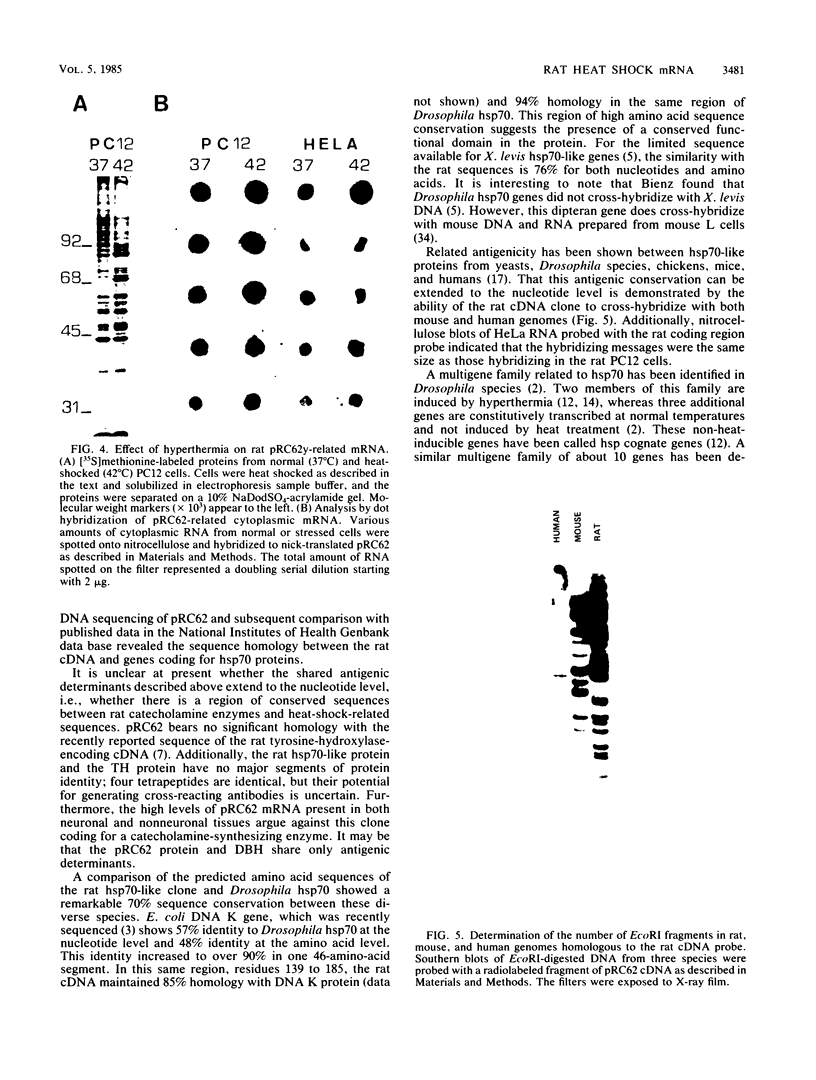
A nearly full-length cDNA clone isolated from the rat pheochromocytoma cell line, PC12, revealed extensive nucleotide sequence similarity between the rat cDNA and the Drosophila melanogaster hsp70 gene. The rat recombinant clone encodes a 71,000-dalton protein that is 70% identical with the dipteran hsp70 protein. Remarkably, a truncated segment of this cDNA clone was originally isolated by immunoreactivity with antisera raised to catecholamine-synthesizing enzymes, suggesting that this heat shock protein and these catecholamine enzymes shared antigenic determinants. The rat hsp70-related mRNA is responsible for the production of a constitutive hsp70 protein, because it is present in abundant amounts in various tissues at normal growth temperatures and is only minimally induced by hyperthermia. The rat hsp70-related sequence is part of a multigene family that extends across species to mice and humans.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashburner M., Bonner J. J. The induction of gene activity in drosophilia by heat shock. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila. V. Responses to environmental treatments. Chromosoma. 1970;31(3):356–376. doi: 10.1007/BF00321231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A. Major heat shock gene of Drosophila and the Escherichia coli heat-inducible dnaK gene are homologous. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):848–852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M. Developmental control of the heat shock response in Xenopus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3138–3142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grima B., Lamouroux A., Blanot F., Biguet N. F., Mallet J. Complete coding sequence of rat tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):617–621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenbüchle O., Bovey R., Young R. A. Tissue-specific expression of mouse-alpha-amylase genes: nucleotide sequence of isoenzyme mRNAs from pancreas and salivary gland. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90125-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hightower L. E., White F. P. Cellular responses to stress: comparison of a family of 71--73-kilodalton proteins rapidly synthesized in rat tissue slices and canavanine-treated cells in culture. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Aug;108(2):261–275. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041080216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren R., Livak K., Morimoto R., Freund R., Meselson M. Studies of cloned sequences from four Drosophila heat shock loci. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1359–1370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia T. D., Craig E. A. Drosophila gene related to the major heat shock-induced gene is transcribed at normal temperatures and not induced by heat shock. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):525–529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia T. D., Craig E. A., McCarthy B. J. Sequence of three copies of the gene for the major Drosophila heat shock induced protein and their flanking regions. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):669–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90430-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia T. D., Slater M. R., Craig E. A. Saccharomyces cerevisiae contains a complex multigene family related to the major heat shock-inducible gene of Drosophila. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1388–1398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joh T. H., Baetge E. E., Ross M. E., Reis D. J. Evidence for the existence of homologous gene coding regions for the catecholamine biosynthetic enzymes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 1):327–335. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley P. M., Schlesinger M. J. Antibodies to two major chicken heat shock proteins cross-react with similar proteins in widely divergent species. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;2(3):267–274. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.3.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley P. M., Schlesinger M. J. The effect of amino acid analogues and heat shock on gene expression in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1277–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key J. L., Lin C. Y., Chen Y. M. Heat shock proteins of higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3526–3530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kothary R. K., Jones D., Candido E. P. 70-Kilodalton heat shock polypeptides from rainbow trout: characterization of cDNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1785–1791. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis W. F., Wheeler S. Heat shock response of Dictyostelium. Dev Biol. 1980 Oct;79(2):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe D. G., Fulford W. D., Moran L. A. Mouse and Drosophila genes encoding the major heat shock protein (hsp70) are highly conserved. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1540–1543. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. J., Xuong N. H., Geiduschek E. P. A response of protein synthesis to temperature shift in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5222–5225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley K. L., Mauron A., Raese J., Barchas J. D., Kedes L. Genes for catecholamine biosynthesis: cloning by expression and identification of the cDNA for rat dopamine beta-hydroxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2161–2165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley K., Mauron A., Makk G., Wong D. L., Ciaranello R. D., Barchas J. D., Kedes L. Dopamine beta-hydroxylase rat mRNA: structure, regulation, and tissue localization. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 1):319–325. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Hsp70 accelerates the recovery of nucleolar morphology after heat shock. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3095–3100. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02264.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch W. J., Feramisco J. R. Nuclear and nucleolar localization of the 72,000-dalton heat shock protein in heat-shocked mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4501–4513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]