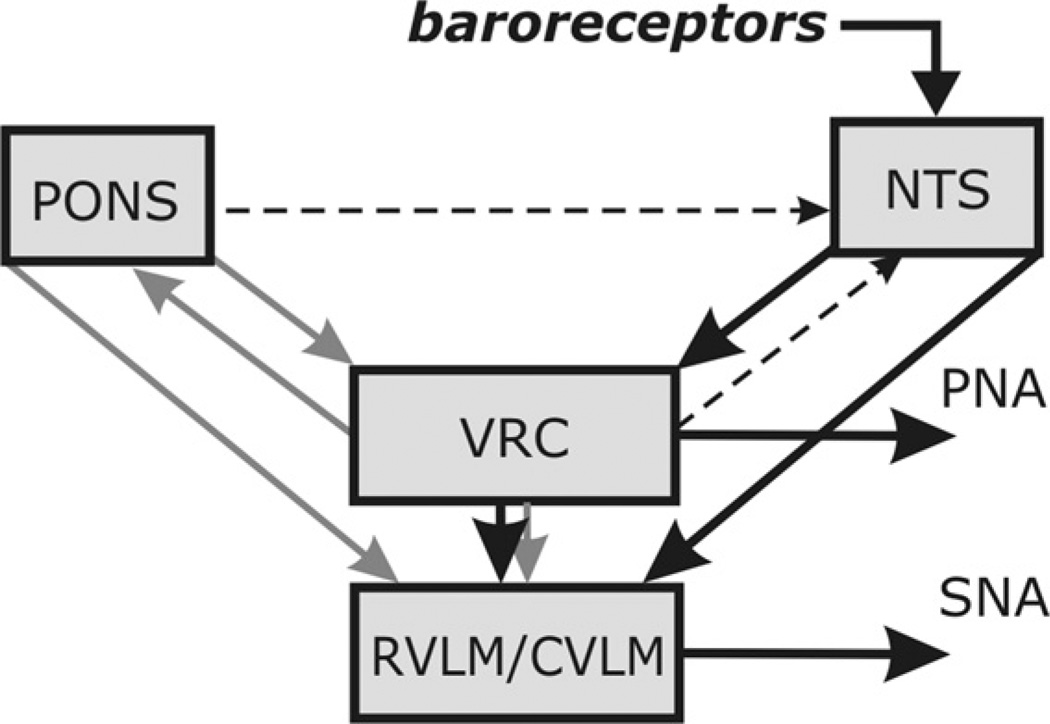
Fig. 2.
Conceptual model of interaction among respiratory-related activity of the ventral respiratory column (VRC), pontine circuits (PONS), sensory network in the nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) and rostral and caudal ventrolateral medulla (RVLM/CVLM). The sympathetic baroreceptor reflex operates via two pathways (thick line, large arrows): one direct pathway includes baroreceptors, NTS baro-sensitive cells and CVLM, which inhibits RVLM and SNA; the other indirect pathway goes from baroreceptors through NTS and VRC, whose post-inspiratory neurones inhibit RVLM and SNA. Grey arrows represent the effects of VRC and PONS on RVLM providing respiratory modulation of SNA. Another grey arrow indicates the effects of VRC on PONS providing respiratory modulation of pontine neurones. Finally, two dashed arrows indicate central suppression of the baroreflex gain during inspiration which potentially can be provided by VRC or pontine neurones see details in the text).